Combined COX-2/PPARγ Expression as Independent Negative Prognosticator for Vulvar Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33802010
- PMCID: PMC8001561
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11030491
Combined COX-2/PPARγ Expression as Independent Negative Prognosticator for Vulvar Cancer Patients
Abstract
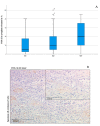
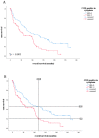
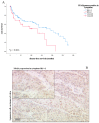
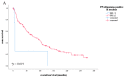
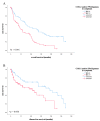
Vulvar cancer incidence numbers have been rising steadily over the past decades. Especially the number of young patients with vulvar cancer increased recently. Therefore, the need to identify new prognostic factors for vulvar carcinoma is more apparent. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has long been an object of scientific interest in the context of carcinogenesis. This enzyme is involved in prostaglandin synthesis and the latter binds to nuclear receptors like PPARγ. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate COX-2- and PPARγ- expression in tissues of vulvar carcinomas and to analyze their relevance as prognostic factors. The cytoplasmatic expression of COX-2 as well as PPARγ is associated with a significantly reduced survival, whereas nuclear expression of PPARγ results in a better survival. Especially the combined expression of both COX-2 and PPARγ in the cytoplasm is an independent negative prognosticator for vulvar cancer patients.
Keywords: COX-2; PPARγ; survival; vulvar cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
S.M. received research support, advisory board, honoraria and travel expenses from AstraZeneca, Clovis, Medac, MSD, PharmaMar, Roche, Sensor Kinesis, Tesaro and Teva. F.T. declares research support, advisory board, honoraria and travel expenses from AstraZeneca, Medac, PharmaMar, Roche and Tesaro. All other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Globocon 2018, Cancer/Vulva (C51). World Health Organization. [(accessed on 12 August 2020)]; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/21-Vulva-fact-sheet.pd....
-
- Madeleine M.M., Daling J.R., Carter J.J., Wipf G.C., Schwartz S.M., McKnight B., Kurman R.J., Beckmann A.M., Hagensee M.E., Galloway D.A. Cofactors with human papillomavirus in a population-based study of vulvar cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997;89:1516–1523. doi: 10.1093/jnci/89.20.1516. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

