Comparative Analysis of Genetic Alterations, HPV-Status, and PD-L1 Expression in Neuroendocrine Carcinomas of the Cervix
- PMID: 33802174
- PMCID: PMC8001835
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061215
Comparative Analysis of Genetic Alterations, HPV-Status, and PD-L1 Expression in Neuroendocrine Carcinomas of the Cervix
Abstract
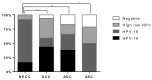
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix (NECC) is a rare and highly aggressive tumor with no efficient treatment. We examined genetic features of NECC and identified potential therapeutic targets. A total of 272 patients with cervical cancer (25 NECC, 180 squamous cell carcinoma, 53 adenocarcinoma, and 14 adenosquamous carcinoma) were enrolled. Somatic hotspot mutations in 50 cancer-related genes were detected using the Ion AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2. Human papillomavirus (HPV)-positivity was examined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based testing and in situ hybridization assays. Programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression was examined using immunohistochemistry. Somatic mutation data for 320 cases of cervical cancer from the Project GENIE database were also analyzed. NECC showed similar (PIK3CA, 32%; TP53, 24%) and distinct (SMAD4, 20%; RET, 16%; EGFR, 12%; APC, 12%) alterations compared with other histological types. The GENIE cohort had similar profiles and RB1 mutations in 27.6% of NECC cases. Eleven (44%) cases had at least one actionable mutation linked to molecular targeted therapies and 14 (56%) cases showed more than one combined positive score for PD-L1 expression. HPV-positivity was observed in all NECC cases with a predominance of HPV-18. We report specific gene mutation profiles for NECC, which can provide a basis for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: HPV; PD-L1; cervical cancer; neuroendocrine carcinomas; next-generation sequencing; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Nagase S., Ohta T., Takahashi F., Enomoto T. 2017 Committee on Gynecologic Oncology of the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Annual Report of the Committee on Gynecologic Oncology, the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology: Annual Patients Report for 2015 and Annual Treatment Report for 2010. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019;45:289–298. doi: 10.1111/jog.13863. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa M., Kasamatsu T., Tsuda H., Fukunaga M., Sakamoto A., Kaku T., Nakanishi T., Hasumi Y., Iwata T., Baba T., et al. Prognostic Factors and Optimal Therapy for Stages I-II Neuroendocrine Carcinomas of the Uterine Cervix: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018;148:139–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.10.027. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

