Identification of Bacterial Blight Resistance Loci in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) against Diverse Xoo Thai Strains by Genome-Wide Association Study
- PMID: 33802191
- PMCID: PMC8001028
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10030518
Identification of Bacterial Blight Resistance Loci in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) against Diverse Xoo Thai Strains by Genome-Wide Association Study
Abstract
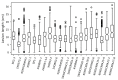
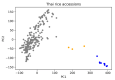
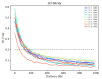
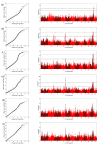
Bacterial leaf blight (BLB) is a serious disease affecting global rice agriculture caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Most resistant rice lines are dependent on single genes that are vulnerable to resistance breakdown caused by pathogen mutation. Here we describe a genome-wide association study of 222 predominantly Thai rice accessions assayed by phenotypic screening against 20 Xoo isolates. Loci corresponding to BLB resistance were detected using >142,000 SNPs. We identified 147 genes according to employed significance thresholds across chromosomes 1-6, 8, 9 and 11. Moreover, 127 of identified genes are located on chromosomal regions outside estimated Linkage Disequilibrium influences of known resistance genes, potentially indicating novel BLB resistance markers. However, significantly associated SNPs only occurred across a maximum of six Xoo isolates indicating that the development of broad-spectrum Xoo strain varieties may prove challenging. Analyses indicated a range of gene functions likely underpinning BLB resistance. In accordance with previous studies of accession panels focusing on indica varieties, our germplasm displays large numbers of SNPs associated with resistance. Despite encouraging data suggesting that many loci contribute to resistance, our findings corroborate previous inferences that multi-strain resistant varieties may not be easily realised in breeding programs without resorting to multi-locus strategies.
Keywords: GWAS; Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; bacterial leaf blight; rice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide Association Analysis Tracks Bacterial Leaf Blight Resistance Loci In Rice Diverse Germplasm.Rice (N Y). 2017 Dec;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12284-017-0147-4. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Rice (N Y). 2017. PMID: 28321828 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study and transcriptome analysis discover new genes for bacterial leaf blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 3;21(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03041-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34082694 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis identifies resistance loci for bacterial blight in a diverse collection of indica rice germplasm.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 29;12(3):e0174598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174598. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28355306 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deployment of Genetic and Genomic Tools Toward Gaining a Better Understanding of Rice-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Interactions for Development of Durable Bacterial Blight Resistant Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 4;11:1152. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01152. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32849710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Rice Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11658. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111658. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior haplotypes towards the development of blast and bacterial blight-resistant rice.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 28;15:1272326. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1272326. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481398 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Pathogenicity Loci in Magnaporthe oryzae Using GWAS with Neck Blast Phenotypic Data.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 20;13(5):916. doi: 10.3390/genes13050916. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627301 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of leaf-related traits in tea plant in Guizhou based on genotyping-by-sequencing.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Apr 12;23(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04192-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37046207 Free PMC article.
-
riceExplorer: Uncovering the Hidden Potential of a National Genomic Resource Against a Global Database.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 29;13:781153. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.781153. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35574109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huerta A.I., Delorean E.E., Bossa-Castro A.M., Tonnessen B.W., Raghavan C., Corral R., Pérez-Quintero Á.L., Leung H., Verdier V., Leach J.E. Resistance and susceptibility QTL identified in a rice MAGIC population by screening with a minor-effect virulence factor from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021;19:51–63. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mew T.W., Cruz C.V., Medalla E.S. Changes in race frequency of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in response to rice cultivars planted in the Philippines. Plant Dis. 1992;76:1029–1032. doi: 10.1094/PD-76-1029. - DOI
-
- Ou S.H. Rice Diseases. Commonwealth Mycological Institute; Kew, UK: 1985.
-
- Saha S., Garg R., Biswas A., Rai A.B. Bacterial diseases of rice: An overview. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015;9:725–736.
-
- Srinivasan B., Gnanamanickam S.S. Identification of a new source of resistance in wild rice, Oryza rufipogon to bacterial blight of rice caused by Indian strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Curr. Sci. 2005;88:1229–1231.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

