Analysis of Brain Functions in Men with Prostate Cancer under Androgen Deprivation Therapy: A One-Year Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 33802213
- PMCID: PMC8000211
- DOI: 10.3390/life11030227
Analysis of Brain Functions in Men with Prostate Cancer under Androgen Deprivation Therapy: A One-Year Longitudinal Study
Abstract
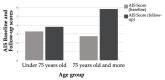
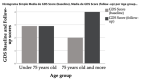
The relationship between cognitive decline and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) under luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogues is unclear, and there is a scarcity of longitudinal studies considering the interaction between cognition, depressive symptoms and sleep quality in men with prostate cancer (PCa) treated with ADT. This study aimed to determine if there were differences in the scores obtained in cognitive assessment, depressive symptoms, and sleep quality after one year of ADT and determine the interrelations between sleep, mood, and cognitive status. A prospective longitudinal observational study was designed, in which a cohort of men (mean age was 70.8 years) newly treated with androgen-deprivation therapy was assessed in the first six months of treatment and 12 months later. Analysis of cognitive function by the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores indicated a significant (p < 0.05) increase after one year of treatment and by the Brief Scale for Cognitive Evaluation (BCog) scores indicated no changes in the scores before and after one year of treatment. Analysis of depressive symptoms with the Geriatric Depression Scale and sleep quality with the Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS) scores showed significant (p < 0.05) changes after one year of treatment with ADT, with men describing more depressive symptoms and more sleep disturbances. No statistically significant differences were found in the cognitive performance between men with impaired sleep or depression results and those without them. Our study showed no clinical evidence of the relationship between ADT under luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogues and cognitive deterioration in 1-year follow-up, but there are impairments in the sleep quality in men with PCa undergoing ADT and an increase in depressive symptoms which has important implications for clinicians as they would impair quality of life and adherence to treatment.
Keywords: androgen-deprivation therapy; cognitive function; depression; neurotoxicity; sleep; testosterone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant aromatase inhibitor treatment worsens depressive symptoms and sleep quality in postmenopausal women with localized breast cancer: A one-year follow-up study.Breast. 2022 Dec;66:310-316. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Breast. 2022. PMID: 36462308 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma Androstenedione Concentration Can Discriminate Frail versus Non-Frail Men with Prostate Cancer under Androgen Deprivation Therapy.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 13;13(11):1642. doi: 10.3390/biom13111642. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002324 Free PMC article.
-
Depressive symptoms are found to be potential adverse effects of androgen deprivation therapy in older prostate cancer patients: A 15-month prospective, observational study.Psychooncology. 2017 Dec;26(12):2238-2244. doi: 10.1002/pon.4453. Epub 2017 May 31. Psychooncology. 2017. PMID: 28474429
-
Androgen deprivation therapy and risk of cognitive dysfunction in men with prostate cancer: is there a possible link?Prostate Int. 2022 Mar;10(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2021.02.002. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Prostate Int. 2022. PMID: 35510099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive Impacts of Estrogen Treatment in Androgen-Deprived Males: What Needs to be Resolved.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(7):1043-1055. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170313122555. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28294068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Androgen Deprivation Therapy on Cognitive Function of Elderly Men With Prostate Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Sep 12;16(9):e69303. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69303. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39398693 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal steroids during pregnancy and their associations with exposure to lifetime stressful life events, prenatal stress appraisal and psychological functioning.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023 Dec;158:106395. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106395. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37776732 Free PMC article.
-
Marital status and perceived stress in men with advanced prostate cancer: A randomized-controlled trial of cognitive behavioral stress management.J Psychosom Res. 2023 Apr;167:111198. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2023.111198. Epub 2023 Feb 16. J Psychosom Res. 2023. PMID: 36812663 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Focus on Cognitive Function and Mood.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 30;60(1):77. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010077. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38256338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive Impairment in Prostate Cancer Patients Receiving Androgen Deprivation Therapy: A Scoping Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;17(15):2501. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152501. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C., Abate D., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdel-Rahman O., Abdelalim A., Abdoli A., Abdollahpour I., Abdulle A.S.M., et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1749–1768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Psychosocial Services to Cancer Patients/Families in a Community Setting . In: Cancer Care for the Whole Patient: Meeting Psychosocial Health Needs. Adler N.E., Page A.E., editors. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC, USA: 2008. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources