Prone Position in Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 33802479
- PMCID: PMC7959453
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10051046
Prone Position in Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: The prone position (PP) is increasingly used in mechanically ventilated coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients. However, studies investigating the influence of the PP are currently lacking in these patients. This is the first study to investigate the influence of the PP on the oxygenation and decarboxylation in COVID-19 patients.
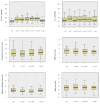
Methods: A prospective bicentric study design was used, and in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients, PP was indicated from a partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2)/fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO2) ratio of <200. Patients were left prone for 16 h each. Pressure levels, FIO2, were adjusted to ensure a PaO2 greater than 60 mmHg. Blood gas analyses were performed before (baseline 0.5 h), during (1/2/5.5/9.5/13 h), and after being in the PP (1 h), the circulatory/ventilation parameters were continuously monitored, and lung compliance (LC) was roughly calculated. Responders were defined compared to the baseline value (PaO2/FIO2 ratio increase of ≥15%; partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) decrease of ≥2%).
Results: 13 patients were included and 36 PP sessions were conducted. Overall, PaO2/FIO2 increased significantly in the PP (p < 0.001). Most PaO2/FIO2 responders (29/36 PP sessions, 77%) were identified 9.5 h after turning prone (14% slow responders), while most PaCO2 responders (15/36 PP sessions, 42%) were identified 13 h after turning prone. A subgroup of patients (interval intubation to PP ≥3 days) showed less PaO2/FIO2 responders (16% vs. 77%). An increase in PaCO2 and minute ventilation in the PP showed a significant negative correlation (p < 0.001). LC (median before the PP = 38 mL/cm H2O; two patients with LC >80 mL/cm H2O) showed a significant positive correlation with the 28 day survival of patients (p = 0.01).
Conclusion: The PP significantly improves oxygenation in COVID-19 ARDS patients. The data suggest that they also benefit most from an early PP. A decrease in minute ventilation may result in fewer PaCO2 responders. LC may be a predictive outcome parameter in COVID-19 patients.
Trial registration: Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: COVID-19 ARDS; lung compliance; prone position.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kluge S., Janssens U., Welte T., Weber-Carstens S., Marx G., Karagiannidis C. Empfehlungen zur inten-sivmedizinischen Therapie von Patienten mit COVID-19 (Recommendations for critically ill patients with COVID-19) Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notf. 2020;115:175–177. doi: 10.1007/s00063-020-00674-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

