Foam Cells as Therapeutic Targets in Atherosclerosis with a Focus on the Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs
- PMID: 33802600
- PMCID: PMC7961492
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052529
Foam Cells as Therapeutic Targets in Atherosclerosis with a Focus on the Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a major cause of human cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of mortality around the world. Various physiological and pathological processes are involved, including chronic inflammation, dysregulation of lipid metabolism, development of an environment characterized by oxidative stress and improper immune responses. Accordingly, the expansion of novel targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis is necessary. In this study, we focus on the role of foam cells in the development of atherosclerosis. The specific therapeutic goals associated with each stage in the formation of foam cells and the development of atherosclerosis will be considered. Processing and metabolism of cholesterol in the macrophage is one of the main steps in foam cell formation. Cholesterol processing involves lipid uptake, cholesterol esterification and cholesterol efflux, which ultimately leads to cholesterol equilibrium in the macrophage. Recently, many preclinical studies have appeared concerning the role of non-encoding RNAs in the formation of atherosclerotic lesions. Non-encoding RNAs, especially microRNAs, are considered regulators of lipid metabolism by affecting the expression of genes involved in the uptake (e.g., CD36 and LOX1) esterification (ACAT1) and efflux (ABCA1, ABCG1) of cholesterol. They are also able to regulate inflammatory pathways, produce cytokines and mediate foam cell apoptosis. We have reviewed important preclinical evidence of their therapeutic targeting in atherosclerosis, with a special focus on foam cell formation.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; foam cell formation; lipid metabolism; noncoding RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Maciej Banach: speakers bureau: Abbott/Mylan, Abbott Vascular, Actavis, Akcea, Amgen, Biofarm, KRKA, MSD, Polpharma, Sanofi Aventis, Servier and Valeant; consultant to Abbott Vascular, Akcea, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, Freia Pharmaceuticals, Lilly, MSD, Polfarmex, Resverlogix, Sanofi-Aventis; Grants from Sanofi and Valeant. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
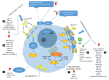
 = decrease,
= decrease,  = increase.
= increase.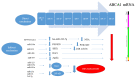
References
-
- Gliozzi M., Scicchitano M., Bosco F., Musolino V., Carresi C., Scarano F., Maiuolo J., Nucera S., Maretta A., Paone S. Modulation of nitric oxide synthases by oxidized LDLs: Role in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3294. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133294. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

