Phytogenic Water Additives Improve Broiler Growth Performance via Modulation of Intermediary Metabolism-Related Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 33803312
- PMCID: PMC7999555
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11030750
Phytogenic Water Additives Improve Broiler Growth Performance via Modulation of Intermediary Metabolism-Related Signaling Pathways
Abstract
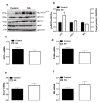
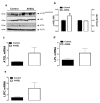
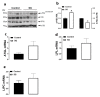
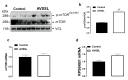
A ban on the use of antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) has fueled and promoted scientific research towards the identification of reliable and effective alternatives. The supplementation of phytogenics AV/SSL12 (AVSSL) and Superliv Gold (SG) in water has been shown to improve broiler feed efficiency (FE) via modulation of hypothalamic neuropeptides. However, their effects on peripheral metabolic pathways are still unknown. The present study was undertaken to determine the effects of AVSSL and SG on lipid and protein metabolism-associated pathways in various tissues. Day-old male Cobb 500 chicks (n = 288) were randomly assigned to 3 treatment groups, with 8 replicates of 12 birds each. The treatment groups were fed a basal diet and supplemented with AVSSL or SG in the drinking water at a rate of 2, 4, and 7 mL/100 birds/d during the starter, grower, and finisher phases, respectively. The control group were fed a basal diet with no additive supplementation. On d 35, liver, adipose, and muscle tissue were collected from one bird per pen (8 birds/group). Data were analyzed using Student's T-test to compare one treatment group to the control using Graph Pad Prism version 6.0 for Windows. In the liver, the levels of phosphorylated acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha (ACCα) were significantly increased in both the AVSSL and SG groups compared to the control. The hepatic expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) was significantly downregulated in both treated groups compared to the control. AVSSL supplementation downregulated the hepatic expression of SREBP-2 and adiponectin (AdipoQ), while SG administration upregulated hepatic AdipoR1/R2 mRNA abundances compared to the untreated group. Both AVSSL and SG treatments upregulated hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1) gene expression compared to their untreated counterparts. In the adipose tissue, the levels of phosphorylated hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) at Ser855/554 site were increased in both the AVSSL and SG groups compared to the control. However, ATGL protein expression was decreased in SG compared to the untreated group. In the muscle, the levels of phosphorylated mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) were increased in the AVSSL, but decreased in the SG group compared to the control. Collectively, these data indicate that supplementation of the phytogenics AVSSL and SG in water reduced hepatic lipogenesis-related proteins and increased adipose tissue lipolysis- and muscle protein synthesis-associated targets, which might explain, at least partially, the improvement in FE observed in previous research.
Keywords: broiler chickens; lipogenesis; lipolysis; phytogenic water additives; protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
B.G. is employed by company Ayurvet Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Ayurvet Ltd. had no role in conducting the research, generating the data, interpreting the results, or writing the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytogenic feed additives improve broiler feed efficiency via modulation of intermediary lipid and protein metabolism-related signaling pathways.Poult Sci. 2021 Mar;100(3):100963. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.12.060. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 33652544 Free PMC article.
-
Phytogenic feed- and water-additives improve feed efficiency in broilers via modulation of (an)orexigenic hypothalamic neuropeptide expression.Neuropeptides. 2020 Jun;81:102005. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2020.102005. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Neuropeptides. 2020. PMID: 31926603
-
Effects of phytogenic additives on meat quality traits in broiler chickens1.J Anim Sci. 2018 Sep 7;96(9):3757-3767. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky238. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 30184154 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Mild Cold Conditioning Modulates the Expression of Hypothalamic Neuropeptide and Intermediary Metabolic-Related Genes and Improves Growth Performances in Young Chicks.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0142319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142319. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26569484 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of phytogenic feed additives on the reproductive performance of animals.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Oct;28(10):5816-5822. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.045. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34588896 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of dietary vitamin E and selenium supplementation on broilers subjected to heat stress, Part II: oxidative stress, immune response, gut integrity, and intestinal microbiota.Poult Sci. 2022 Jun;101(6):101858. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101858. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35468426 Free PMC article.
-
Inclusion of a microencapsulated pepper, cashew nut, and copaiba essential oils blend in broiler feed: evaluation of performance and nutrient metabolizability.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025 Jun 26;57(6):288. doi: 10.1007/s11250-025-04538-w. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2025. PMID: 40569351 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of dietary vitamin E and selenium supplementation on broilers subjected to heat stress, Part I: Growth performance, body composition and intestinal nutrient transporters.Poult Sci. 2022 Jun;101(6):101857. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101857. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35461066 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a microencapsulated phyto/phycogenic blend supplementation on growth performance, processing parameters, meat quality, and sensory profile in male broilers.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Mar 28;11:1382535. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1382535. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38605922 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of the thermoregulatory potential of in ovo delivered bioactive substances (probiotic, folic acid, and essential oil) in broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2023 May;102(5):102602. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102602. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36924590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emami N.K., Calik A., White M.B., Kimminau E.A., Dalloul R.A. Effect of Probiotics and Multi-Component Feed Additives on Microbiota, Gut Barrier and Immune Responses in Broiler Chickens During Subclinical Necrotic Enteritis. Front. Veter-Sci. 2020;7:572142. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.572142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

