Bacillus megaterium-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Antifungal Activity against Rhizoctonia solani in Faba Bean Plants
- PMID: 33803321
- PMCID: PMC8001679
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7030195
Bacillus megaterium-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Antifungal Activity against Rhizoctonia solani in Faba Bean Plants
Abstract
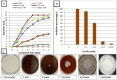
Rhizoctonia root-rot disease causes severe economic losses in a wide range of crops, including Vicia faba worldwide. Currently, biosynthesized nanoparticles have become super-growth promoters as well as antifungal agents. In this study, biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) have been examined as growth promoters as well as antifungal agents against Rhizoctonia solani RCMB 031001 in vitro and in vivo. Se-NPs were synthesized biologically by Bacillus megaterium ATCC 55000 and characterized by using UV-Vis spectroscopy, XRD, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging. TEM and DLS images showed that Se-NPs are mono-dispersed spheres with a mean diameter of 41.2 nm. Se-NPs improved healthy Vicia faba cv. Giza 716 seed germination, morphological, metabolic indicators, and yield. Furthermore, Se-NPs exhibited influential antifungal activity against R. solani in vitro as well as in vivo. Results revealed that minimum inhibition and minimum fungicidal concentrations of Se-NPs were 0.0625 and 1 mM, respectively. Moreover, Se-NPs were able to decrease the pre-and post-emergence of R. solani damping-off and minimize the severity of root rot disease. The most effective treatment method is found when soaking and spraying were used with each other followed by spraying and then soaking individually. Likewise, Se-NPs improve morphological and metabolic indicators and yield significantly compared with infected control. In conclusion, biosynthesized Se-NPs by B. megaterium ATCC 55000 are a promising and effective agent against R. solani damping-off and root rot diseases in Vicia faba as well as plant growth inducer.
Keywords: R. solani; Se-NPs; Vicia faba; nano-biosynthesis; plant disease; plant promotion; root rot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Khalil A.M.A., Hashem A.H., Abdelaziz A.M. Occurrence of toxigenic Penicillium polonicum in retail green table olives from the Saudi Arabia market. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019;21:101314. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101314. - DOI
-
- Bramhanwade K., Shende S., Bonde S., Gade A., Rai M. Fungicidal activity of Cu nanoparticles against Fusarium causing crop diseases. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016;14:229–235. doi: 10.1007/s10311-015-0543-1. - DOI
-
- Srivastava S., Bist V., Srivastava S., Singh P.C., Trivedi P.K., Asif M.H., Chauhan P.S., Nautiyal C.S. Unraveling aspects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens mediated enhanced production of rice under biotic stress of Rhizoctonia solani. Front. Plant Sci. 2016;7:587. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00587. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

