Increased Presence of Complement Factors and Mast Cells in Alveolar Bone and Tooth Resorption
- PMID: 33803323
- PMCID: PMC7967164
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052759
Increased Presence of Complement Factors and Mast Cells in Alveolar Bone and Tooth Resorption
Abstract
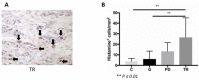
Periodontitis is the inflammatory destruction of the tooth-surrounding and -supporting tissue, resulting at worst in tooth loss. Another locally aggressive disease of the oral cavity is tooth resorption (TR). This is associated with the destruction of the dental mineralized tissue. However, the underlying pathomechanisms remain unknown. The complement system, as well as mast cells (MCs), are known to be involved in osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. The complement factors C3 and C5 were previously identified as key players in periodontal disease. Therefore, we hypothesize that complement factors and MCs might play a role in alveolar bone and tooth resorption. To investigate this, we used the cat as a model because of the naturally occurring high prevalence of both these disorders in this species. Teeth, gingiva samples and serum were collected from domestic cats, which had an appointment for dental treatment under anesthesia, as well as from healthy cats. Histological analyses, immunohistochemical staining and the CH-50 and AH-50 assays revealed increased numbers of osteoclasts and MCs, as well as complement activity in cats with TR. Calcifications score in the gingiva was highest in animals that suffer from TR. This indicates that MCs and the complement system are involved in the destruction of the mineralized tissue in this condition.
Keywords: complement system; mast cells; osteoclasts; periodontitis; tooth resorption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interactive effects of periodontitis and orthodontic tooth movement on dental root resorption, tooth movement velocity and alveolar bone loss in a rat model.Ann Anat. 2017 Mar;210:32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Ann Anat. 2017. PMID: 27838559
-
Presence and quantification of mast cells in the gingiva of cats with tooth resorption, periodontitis and chronic stomatitis.Arch Oral Biol. 2010 Feb;55(2):148-54. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2009.11.004. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Arch Oral Biol. 2010. PMID: 20018273
-
Expression of adhesion molecules during tooth resorption in feline teeth: a model system for aggressive osteoclastic activity.J Dent Res. 1996 Sep;75(9):1650-7. doi: 10.1177/00220345960750090601. J Dent Res. 1996. PMID: 8952617
-
The effects of tumour necrosis factor-α on bone cells involved in periodontal alveolar bone loss; osteoclasts, osteoblasts and osteocytes.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Oct;51(5):549-66. doi: 10.1111/jre.12339. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26667183 Review.
-
Complement inhibition in pre-clinical models of periodontitis and prospects for clinical application.Semin Immunol. 2016 Jun;28(3):285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Semin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27021500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Osteoclastogenesis and Osteogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 15;23(12):6659. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126659. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743101 Free PMC article.
-
Altered early immune response after fracture and traumatic brain injury.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 25;14:1074207. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1074207. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36761764 Free PMC article.
-
Complement System and Alarmin HMGB1 Crosstalk: For Better or Worse.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 28;13:869720. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869720. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35572583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolf H., Rateitschak-Pluss E., Rateitschak K.H. Color Atlas of Dental Medicine: Periodontology. Georg Thieme Verlag; Stuttgart, Germany: 2005.
-
- Shope B., Carle D. Tooth Resorptions in Dogs and Cats. [(accessed on 14 May 2017)]; Available online: http://blog.vetbloom.com/dentistry/tooth-resorption-in-dogs-and-cats/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

