Development of Rapid and High-Precision Colorimetric Device for Organophosphorus Pesticide Detection Based on Microfluidic Mixer Chip
- PMID: 33803445
- PMCID: PMC8000396
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12030290
Development of Rapid and High-Precision Colorimetric Device for Organophosphorus Pesticide Detection Based on Microfluidic Mixer Chip
Abstract
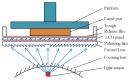
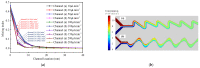
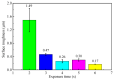
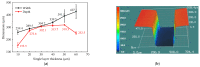
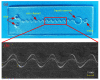
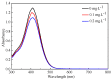
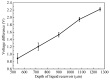
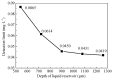
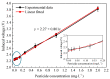
The excessive pesticide residues in cereals, fruit and vegetables is a big threat to human health, and it is necessary to develop a portable, low-cost and high-precision pesticide residue detection scheme to replace the large-scale laboratory testing equipment for rapid detection of pesticide residues. In this study, a colorimetric device for rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticide residues with high precision based on a microfluidic mixer chip was proposed. The microchannel structure with high mixing efficiency was determined by fluid dynamics simulation, while the corresponding microfluidic mixer chip was designed. The microfluidic mixer chip was prepared by a self-developed liquid crystal display (LCD) mask photo-curing machine. The influence of printing parameters on the accuracy of the prepared chip was investigated. The light source with the optimal wavelength of the device was determined by absorption spectrum measurement, and the relationship between the liquid reservoir depth and detection limit was studied by experiments. The correspondence between pesticide concentration and induced voltage was derived. The minimum detection concentration of the device could reach 0.045 mg·L-1 and the average detection time was reduced to 60 s. The results provide a theoretical and experimental basis for portable and high-precision detection of pesticide residues.
Keywords: LCD mask photo-curing; colorimetric device; microfluidics; organophosphorus pesticide residues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pump-Free Microfluidic Rapid Mixer Combined with a Paper-Based Channel.ACS Sens. 2020 Jul 24;5(7):2230-2238. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c00937. Epub 2020 Jul 13. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32583663
-
Electrochemical Detection of Ascorbic Acid in Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Chip.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;13(9):1479. doi: 10.3390/mi13091479. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36144101 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Portable Residual Chlorine Detection Device with a Combination of Microfluidic Chips and LS-BP Algorithm to Achieve Accurate Detection of Residual Chlorine in Water.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Aug 18;15(8):1045. doi: 10.3390/mi15081045. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39203696 Free PMC article.
-
A review on microfluidics in the detection of food pesticide residues.Electrophoresis. 2020 Jun;41(10-11):821-832. doi: 10.1002/elps.201900209. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Electrophoresis. 2020. PMID: 31525822 Review.
-
Research progress on pesticide residue detection based on microfluidic technology.Electrophoresis. 2023 Sep;44(17-18):1377-1404. doi: 10.1002/elps.202300048. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Electrophoresis. 2023. PMID: 37496295 Review.
Cited by
-
Acoustohydrodynamic micromixers: Basic mixing principles, programmable mixing prospectives, and biomedical applications.Biomicrofluidics. 2024 Apr 18;18(2):021505. doi: 10.1063/5.0179750. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2024. PMID: 38659428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-efficient fabrication method for 3D-printed microfluidic devices.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 24;12(1):1233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05350-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35075184 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical investigating the impact of fluid properties and oscillation frequency on micro mixer efficiency.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 17;11(1):e41290. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41290. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811278 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Characterization of Pendimethalin Microcapsules Based on Microfluidic Technology.ACS Omega. 2021 Dec 5;6(49):34160-34172. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05903. eCollection 2021 Dec 14. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34926964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yassine A., Omar B., Karine G.S. Study of the degradation of an organophosphorus pesticide using electrogenerated hydroxyl radicals or heat-activated persulfate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018;208:27–33.
-
- Zhe Z., Godefroy S.B., Hanyang L., Baoguo S., Yongxiang F. Transformation of china’s food safety standard setting system—Review of 50 years of change, opportunities and challenges ahead. Food Control. 2018;93:106–111.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

