Mechanical Properties and Reliability of Parametrically Designed Architected Materials Using Urethane Elastomers
- PMID: 33803487
- PMCID: PMC7967173
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13050842
Mechanical Properties and Reliability of Parametrically Designed Architected Materials Using Urethane Elastomers
Abstract
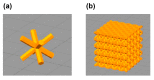
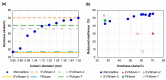
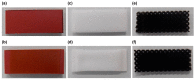
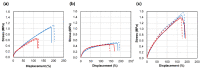
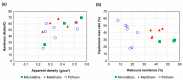
Achieving multiple physical properties from a single material through three-dimensional (3D) printing is important for manufacturing applications. In addition, industrial-level durability and reliability is necessary for realizing individualized manufacturing of devices using 3D printers. We investigated the properties of architected materials composed of ultraviolet (UV)-cured urethane elastomers for use as insoles. The durability and reliability of microlattice and metafoam architected materials were compared with those composed of various foamed materials currently used in medical insoles. The hardness of the architected materials was able to be continuously adjusted by controlling the design parameters, and the combination of the two materials was effective in controlling rebound resilience. In particular, the features of the architected materials were helpful for customizing the insole properties, such as hardness, propulsive force, and shock absorption, according to the user's needs. Further, using elastomer as a component led to better results in fatigue testing and UV resistance compared with the plastic foam currently used for medical purposes. Specifically, polyethylene and ethylene vinyl acetate were deformed in the fatigue test, and polyurethane was mechanically deteriorated by UV rays. Therefore, these architected materials are expected to be reliable for long-term use in insoles.
Keywords: 3D printing; Asker hardness; additive manufacturing; architected material; elastomer; foam; insole; lattice; metamaterial; reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was conducted with research funding from JSR Corporation, to which J.M., Y.A., S.K., and K.M. belong.
Figures






References
-
- Pham D.T., Gault R.S. A comparison of rapid prototyping technologies. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1998;38:1257–1287. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(97)00137-5. - DOI
-
- Rayna T., Striukova L. From rapid prototyping to home fabrication: How 3D printing is changing business model innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2016;102:214–224. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.07.023. - DOI
-
- HDürr H., Pilz R., SaadEleser N. Rapid tooling of EDM electrodes by means of selective laser sintering. Comput. Ind. 1999;39:35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0166-3615(98)00123-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

