SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Transmission Clusters and Containment Measures in Ten European Regions during the First Pandemic Wave
- PMID: 33803490
- PMCID: PMC8001481
- DOI: 10.3390/life11030219
SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Transmission Clusters and Containment Measures in Ten European Regions during the First Pandemic Wave
Abstract
Background: The spatiotemporal profiling of molecular transmission clusters (MTCs) using viral genomic data can effectively identify transmission networks in order to inform public health actions targeting SARS-CoV-2 spread.
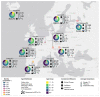
Methods: We used whole genome SARS-CoV-2 sequences derived from ten European regions belonging to eight countries to perform phylogenetic and phylodynamic analysis. We developed dedicated bioinformatics pipelines to identify regional MTCs and to assess demographic factors potentially associated with their formation.
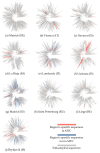
Results: The total number and the scale of MTCs varied from small household clusters identified in all regions, to a super-spreading event found in Uusimaa-FI. Specific age groups were more likely to belong to MTCs in different regions. The clustered sequences referring to the age groups 50-100 years old (y.o.) were increased in all regions two weeks after the establishment of the lockdown, while those referring to the age group 0-19 y.o. decreased only in those regions where schools' closure was combined with a lockdown.
Conclusions: The spatiotemporal profiling of the SARS-CoV-2 MTCs can be a useful tool to monitor the effectiveness of the interventions and to reveal cryptic transmissions that have not been identified through contact tracing.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; clusters; molecular epidemiology; molecular transmission clusters; pandemic; phylodynamics; phylogenetics; transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou H., Chen X., Hu T., Li J., Song H., Liu Y., Wang P., Liu D., Yang J., Holmes E.C., et al. A novel bat coronavirus closely related to SARS-CoV-2 contains natural insertions at the S1/S2 cleavage site of the spike protein. Curr. Biol. 2020;30:2196–2203. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

