Ecological and Biotechnological Aspects of Pigmented Microbes: A Way Forward in Development of Food and Pharmaceutical Grade Pigments
- PMID: 33803896
- PMCID: PMC8003166
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9030637
Ecological and Biotechnological Aspects of Pigmented Microbes: A Way Forward in Development of Food and Pharmaceutical Grade Pigments
Abstract
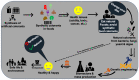
Microbial pigments play multiple roles in the ecosystem construction, survival, and fitness of all kinds of organisms. Considerably, microbial (bacteria, fungi, yeast, and microalgae) pigments offer a wide array of food, drug, colorants, dyes, and imaging applications. In contrast to the natural pigments from microbes, synthetic colorants are widely used due to high production, high intensity, and low cost. Nevertheless, natural pigments are gaining more demand over synthetic pigments as synthetic pigments have demonstrated side effects on human health. Therefore, research on microbial pigments needs to be extended, explored, and exploited to find potential industrial applications. In this review, the evolutionary aspects, the spatial significance of important pigments, biomedical applications, research gaps, and future perspectives are detailed briefly. The pathogenic nature of some pigmented bacteria is also detailed for awareness and safe handling. In addition, pigments from macro-organisms are also discussed in some sections for comparison with microbes.
Keywords: biological properties; fluorescent pigments; horizontal gene transfer; pigments evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multifaceted Applications of Microbial Pigments: Current Knowledge, Challenges and Future Directions for Public Health Implications.Microorganisms. 2019 Jun 28;7(7):186. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7070186. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31261756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pigment production by cold-adapted bacteria and fungi: colorful tale of cryosphere with wide range applications.Extremophiles. 2020 Jul;24(4):447-473. doi: 10.1007/s00792-020-01180-2. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Extremophiles. 2020. PMID: 32488508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization and application of microbial pigments in foods as natural colors.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Oct 28:1-30. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2417802. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39466660 Review.
-
Fungal Pigments: Potential Coloring Compounds for Wide Ranging Applications in Textile Dyeing.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 May 20;6(2):68. doi: 10.3390/jof6020068. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32443916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Pigments in the Food Industry-Challenges and the Way Forward.Front Nutr. 2019 Mar 5;6:7. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00007. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30891448 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring bioactive compound origins: Profiling gene cluster signatures related to biosynthesis in microbiomes of Sof Umer Cave, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 6;20(3):e0315536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315536. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40048434 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Pigment Production by Filamentous Fungal Strains under Submerged (SmF) and Surface Adhesion Fermentation (SAF).J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;9(1):48. doi: 10.3390/jof9010048. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36675869 Free PMC article.
-
Blue Microbiology-Aquatic Microbial Resources for Sustainable Life on Earth.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 22;11(3):808. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030808. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985381 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Pigments: Carotenoids, Riboflavin, and Polyketides with Diverse Applications.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;9(4):454. doi: 10.3390/jof9040454. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37108908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pigment production by a newly isolated strain Pycnoporus sanguineus SYBC-L7 in solid-state fermentation.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1015913. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1015913. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scholes G.D., Mirkovic T., Turner D.B., Fassioli F., Buchleitner A. Solar light harvesting by energy transfer: From ecology to coherence. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012;5:9374–9393. doi: 10.1039/c2ee23013e. - DOI
-
- Kamio M., Grimes T.V., Hutchins M.H., van Dam R., Derby C.D. The purple pigment aplysioviolin in sea hare ink deters predatory blue crabs through their chemical senses. Anim. Behav. 2010;80:89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2010.04.003. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

