The Effect of NUDT15, TPMT, APEX1, and ITPA Genetic Variations on Mercaptopurine Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 33804051
- PMCID: PMC7998516
- DOI: 10.3390/children8030224
The Effect of NUDT15, TPMT, APEX1, and ITPA Genetic Variations on Mercaptopurine Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
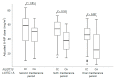
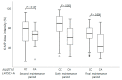
Mercaptopurine (MP) is a commonly used maintenance regimen for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, 6-MP has a narrow therapeutic index, which causes dose-limiting toxicities in hematopoietic tissues. Recent studies reported several candidate pharmacogenetic markers such as TPMT, NUDT15, ITPA, and APEX1, which predict the possibility of 6-MP related toxicities. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of major variants of these genes on 6-MP intolerances and toxicities in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients. A total of 83 pediatric ALL patients were included (56 males and 27 females). The NUDT15 c.415C>T (rs116855232), NUDT15 c.55_56insGAGTCG (rs746071566), ITPA c.94C>A (rs1127354), ITPA c.IVS2+21A>C (rs7270101), APEX c.190A>G (rs2307486), and TPMT variants were analyzed by sanger sequencing. Correlations between indexes of 6-MP-related toxicities or 6-MP intolerance (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] at several time point, days of ANC < 1 × 103/mm3, days of ANC < 0.5 × 103/mm3, frequency of febrile neutropenia, maximum AST and ALT, 6-MP dose and 6-MP dose intensity during maintenance therapy) and genetic variations were analyzed. The NUDT15 c.415C>T allele carrier showed significantly low 6-MP doses at the final maintenance therapy period than the wild type carrier (p = 0.007). The 6-MP dose intensities at the sixth and final maintenance period were also significantly low in NUDT15 c.415C>T carriers (p = 0.003 and 0.008, respectively). However, indexes for neutropenia, days of febrile neutropenia, maximum AST, and ALT levels were not associated with the presence of c.415C>T as well as other analyzed variants. When analyzing the effect of the coexistence of NUDT15 c.415C>T and ITPA c.94C>A, no significant differences were found between the NUDT15 c.415C>T carrier and carrier with both variations. The NUDT15 c.415C>T was the most useful marker to predict 6-MP intolerance among analyzed variants in our study population. Although we could not find association of those variants with 6-MP induced toxicities and the synergistic effects of those variants, a well-planed larger scale study would be helpful in clarifying new candidates and their clinical effects.
Keywords: 6-mercaptopurine; APEX; ITPA; NUDT15; TPMT; acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatia S., Landier W., Hageman L., Chen Y., Kim H., Sun C.L., Kornegay N., Evans W.E., Angiolillo A.L., Bostrom B., et al. Systemic Exposure to Thiopurines and Risk of Relapse in Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1:287–295. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wahlund M., Nilsson A., Kahlin A.Z., Broliden K., Myrberg I.H., Appell M.L., Berggren A. The Role of TPMT, ITPA, and NUDT15 Variants during Mercaptopurine Treatment of Swedish Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Pediatr. 2020;216:150–157.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.09.024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

