Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction: An Overview on Cellular Processes, Molecular Pathways, Clinical Evaluation and Prognostic Value
- PMID: 33804308
- PMCID: PMC7931027
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci9010016
Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction: An Overview on Cellular Processes, Molecular Pathways, Clinical Evaluation and Prognostic Value
Abstract
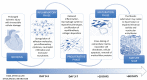
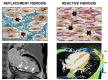
The ischemic injury caused by myocardial infarction activates a complex healing process wherein a powerful inflammatory response and a reparative phase follow and balance each other. An intricate network of mediators finely orchestrate a large variety of cellular subtypes throughout molecular signaling pathways that determine the intensity and duration of each phase. At the end of this process, the necrotic tissue is replaced with a fibrotic scar whose quality strictly depends on the delicate balance resulting from the interaction between multiple actors involved in fibrogenesis. An inflammatory or reparative dysregulation, both in term of excess and deficiency, may cause ventricular dysfunction and life-threatening arrhythmias that heavily affect clinical outcome. This review discusses cellular process and molecular signaling pathways that determine fibrosis and the imaging technique that can characterize the clinical impact of this process in-vivo.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance; fibrosis; inflammation; molecular pathways; myocardial infarction; prognostic value.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

