Tetracycline-Resistant Bacteria Selected from Water and Zebrafish after Antibiotic Exposure
- PMID: 33804606
- PMCID: PMC8003806
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18063218
Tetracycline-Resistant Bacteria Selected from Water and Zebrafish after Antibiotic Exposure
Abstract
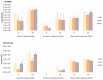
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens due to worldwide antibiotic use is raising concern in several settings, including aquaculture. In this work, the selection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) was evaluated after exposure of zebrafish to oxytetracycline (OTC) for two months, followed by a recovery period. The selection of ARB in water and fish was determined using selective media. The abundance of tetA genes was estimated through qPCR. Higher prevalence of ARB was measured in all samples exposed to the antibiotic when compared to control samples, although statistical significance was only achieved five days after exposure. Isolates recovered from samples exposed to the antibiotic were affiliated with Pseudomonas and Stenotrophomonas. Various antibiotic susceptibility profiles were detected and 37% of the isolates displayed multidrug resistance (MDR). The selection of the tetA gene was confirmed by qPCR at the highest OTC concentration tested. Two MDR isolates, tested using zebrafish embryos, caused significant mortality, indicating a potential impact on fish health and survival. Overall, our work highlights the potential impact of antibiotic contamination in the selection of potential pathogenic ARB and ARGS.
Keywords: Danio rerio; microcosm; multidrug resistance; pathogenicity test; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Føre M., Frank K., Norton T., Svendsen E., Arve J., Dempster T., Eguiraun H., Watson W., Stahl A., Magne L., et al. Precision fish farming: A new framework to improve production in aquaculture. Biosyst. Eng. 2018;173:176–193. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2017.10.014. - DOI
-
- European Medicines Agency Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2017. Trends from 2010 to 2017. (Ema/294674/2019) [(accessed on 5 February 2020)];2019 Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicro....
-
- Cravedi J.-P., Choubert G., Delous G. Digestibility of chloramphenicol, oxolinic acid and oxytetracycline in rainbow trout and influence of these antibiotics on lipid digestibility. Aquaculture. 1987;60:133–141. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(87)90305-X. - DOI
-
- Chen H., Liu S., Xu X.R., Liu S.S., Zhou G.J., Sun K.F., Zhao J.L., Ying G.G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015;90:181–187. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.10.053. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Monteiro S.H., Francisco J.G., Andrade G.C.R.M., Botelho R.G., Figueiredo L.A., Tornisielo V.L. Study of spatial and temporal distribution of antimicrobial in water and sediments from caging fish farms by on-line SPE-LC-MS/MS. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes. 2016;51:634–643. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2016.1181917. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

