The Role of CaMKII and ERK Signaling in Addiction
- PMID: 33804804
- PMCID: PMC8004038
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22063189
The Role of CaMKII and ERK Signaling in Addiction
Abstract
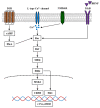
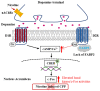
Nicotine is the predominant addictive compound of tobacco and causes the acquisition of dependence through its interactions with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and various neurotransmitter releases in the central nervous system. The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) play a pivotal role in synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. CaMKII is involved in long-term potentiation induction, which underlies the consolidation of learning and memory; however, the roles of CaMKII in nicotine and other psychostimulant-induced addiction still require further investigation. This article reviews the molecular mechanisms and crucial roles of CaMKII and ERK in nicotine and other stimulant drug-induced addiction. We also discuss dopamine (DA) receptor signaling involved in nicotine-induced addiction in the brain reward circuitry. In the last section, we introduce the association of polyunsaturated fatty acids and cellular chaperones of fatty acid-binding protein 3 in the context of nicotine-induced addiction in the mouse nucleus accumbens and provide a novel target for the treatment of drug abuse affecting dopaminergic systems.
Keywords: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; dopamine D1 receptor; dopamine D2 receptor; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; fatty acid-binding protein 3; nicotine-induced addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Forouzanfar M.H., Afshin A., Alexander L.T., Anderson H.R., Bhutta Z.A., Biryukov S., Brauer M., Burnett R., Cercy K., Charlson F.J., et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1659–1724. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reitsma M.B., Fullman N., Ng M., Salama J.S., Abajobir A., Abate K.H., Abbafati C., Abera S.F., Abraham B., Abyu G.Y., et al. Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2017;389:1885–1906. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30819-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

