Transgenic Expression of dsRNA Targeting the Pentalonia nigronervosa acetylcholinesterase Gene in Banana and Plantain Reduces Aphid Populations
- PMID: 33804880
- PMCID: PMC8063806
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10040613
Transgenic Expression of dsRNA Targeting the Pentalonia nigronervosa acetylcholinesterase Gene in Banana and Plantain Reduces Aphid Populations
Abstract
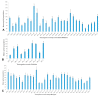
The banana aphid, Pentalonia nigronervosa, is the sole insect vector of banana bunchy top virus (BBTV), the causal agent of banana bunchy top disease. The aphid acquires and transmits BBTV while feeding on infected banana plants. RNA interference (RNAi) enables the generation of pest and disease-resistant crops; however, its effectiveness relies on the identification of pivotal gene sequences to target and silence. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an essential enzyme responsible for the hydrolytic metabolism of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in animals. In this study, the AChE gene of the banana aphid was targeted for silencing by RNAi through transgenic expression of AChE dsRNA in banana and plantain plants. The efficacy of dsRNA was first assessed using an artificial feeding assay. In vitro aphid feeding on a diet containing 7.5% sucrose, and sulfate complexes of trace metals supported aphid growth and reproduction. When AChE dsRNA was included in the diet, a dose of 500 ng/μL was lethal to the aphids. Transgenic banana cv. Cavendish Williams and plantain cvs. Gonja Manjaya and Orishele expressing AChE dsRNA were regenerated and assessed for transgene integration and copy number. When aphids were maintained on elite transgenic events, there was a 67.8%, 46.7%, and 75.6% reduction in aphid populations growing on Cavendish Williams, Gonja Manjaya, and Orishele cultivars, respectively, compared to those raised on nontransgenic control plants. These results suggest that RNAi targeting an essential aphid gene could be a useful means of reducing both aphid infestation and potentially the spread of the disease they transmit.
Keywords: RNA interference; acetylcholinesterase; artificial diet; banana; banana aphid; plantain; sugars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Lowe S., Browne M., Boudjelas S., De Poorter M. 100 of the World’ s Worst Invasive Alien Species. Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG); Auckland, New Zealand: 2000.
-
- Selvarajan R., Balasubramanian V. Host-virus interactions in banana-infecting viruses. In: Gaur R., Hohn T., Sharma P., editors. Plant Virus—Ost Interaction: Molecular Approaches and Viral Evolution. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2014. pp. 57–72.
-
- Jekayinoluwa T., Tripathi J.N., Obiero G., Muge E., Dale J., Tripathi L. Developing Plantain for Resistance to Banana Aphids by RNA Interference. Proceedings. 2020;36:54. doi: 10.3390/proceedings2019036054. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

