Undetected Causes of Death in Hospitalized Elderly with COVID-19: Lessons from Autopsy
- PMID: 33804890
- PMCID: PMC8037274
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071337
Undetected Causes of Death in Hospitalized Elderly with COVID-19: Lessons from Autopsy
Abstract
Background: Mechanisms and causes of death in older patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection are still poorly understood.
Methods: We conducted in a retrospective monocentric study, a clinical chart review and post-mortem examination of patients aged 75 years and older hospitalized in acute care and positive for SARS-CoV-2. Full body autopsy and correlation with clinical findings and suspected causes of death were done.
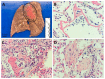
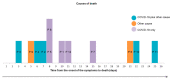
Results: Autopsies were performed in 12 patients (median age 85 years; median of 4 comorbidities, mainly hypertension and cardiovascular disease). All cases showed exudative or proliferative phases of alveolar damage and/or a pattern of organizing pneumonia. Causes of death were concordant in 6 cases (50%), and undetected diagnoses were found in 6. Five patients died from hypoxemic respiratory failure due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), five had another associated diagnosis and two died from alternative causes. Deaths that occurred in the second week were related to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia whereas those occurring earlier were related mainly to heart failure and those occurring later to complications.
Conclusions: Although COVID-19 hypoxemic respiratory failure was the most common cause of death, post-mortem pathological examination revealed that acute decompensation from chronic comorbidities during the first week of COVID-19 and complications in the third week contributed to mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19; autopsy; elderly patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y., Qiu Y., Wang J., Liu Y., Wei Y., et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weekly Epidemiological Update—20 October 2020. [(accessed on 24 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

