GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33804962
- PMCID: PMC8063930
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10040721
GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
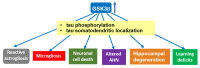
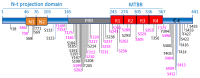
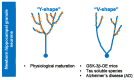
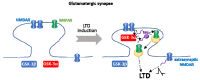
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a ubiquitously expressed serine/threonine kinase with a plethora of substrates. As a modulator of several cellular processes, GSK-3 has a central position in cell metabolism and signaling, with important roles both in physiological and pathological conditions. GSK-3 has been associated with a number of human disorders, such as neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD). GSK-3 contributes to the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, the main component of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), one of the hallmarks of AD. GSK-3 is further involved in the regulation of different neuronal processes that are dysregulated during AD pathogenesis, such as the generation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide or Aβ-induced cell death, axonal transport, cholinergic function, and adult neurogenesis or synaptic function. In this review, we will summarize recent data about GSK-3 involvement in these processes contributing to AD pathology, mostly focusing on the crucial interplay between GSK-3 and tau protein. We further discuss the current development of potential AD therapies targeting GSK-3 or GSK-3-phosphorylated tau.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GSK-3; neurodegeneration; tau phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rylatt D.B., Aitken A., Bilham T., Condon G.D., Embi N., Cohen P. Glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Amino acid sequence at the sites phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase-3, and extension of the N-terminal sequence containing the site phosphorylated by phosphorylase kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980;107:529–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06060.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanger D.P., Hughes K., Woodgett J.R., Brion J.P., Anderton B.H. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer’s disease-like phosphorylation of tau: Generation of paired helical filament epitopes and neuronal localisation of the kinase. Neurosci. Lett. 1992;147:58–62. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90774-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

