COVID-19 and Pneumocystis jirovecii Pulmonary Coinfection-The First Case Confirmed through Autopsy
- PMID: 33804963
- PMCID: PMC8063940
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57040302
COVID-19 and Pneumocystis jirovecii Pulmonary Coinfection-The First Case Confirmed through Autopsy
Abstract
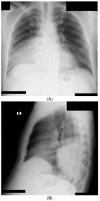
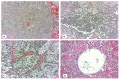
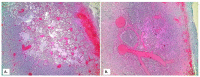
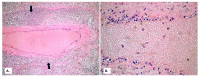
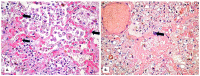
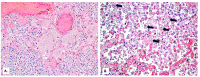
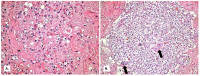
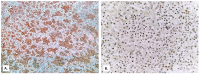
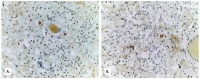
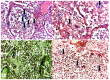
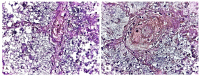
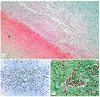
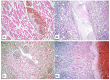
Background: Establishing the diagnosis of COVID-19 and Pneumocystisjirovecii pulmonary coinfection is difficult due to clinical and radiological similarities that exist between the two disorders. For the moment, fungal coinfections are underestimated in COVID-19 patients. Case presentation: We report the case of a 52-year-old male patient, who presented to the emergency department for severe dyspnea and died 17 h later. The RT-PCR test performed at his admission was negative for SARS-CoV-2. Retesting of lung fragments collected during autopsy revealed a positive result for SARS-CoV-2. Histopathological examination showed preexisting lesions, due to comorbidities, as well as recent lesions: massive lung thromboses, alveolar exudate rich in foam cells, suprapleural and intra-alveolar Pneumocystisjirovecii cystic forms, and bilateral adrenal hemorrhage. Conclusion: COVID-19 and P.jirovecii coinfection should be considered, particularly in critically ill patients, and we recommend the systematic search for P. jirovecii in respiratory samples.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pneumocystis jirovecii; SARS-CoV-2; autopsy; coinfection; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Messina F.A., Marin E., Caceres D.H., Romero M., Depardo R., Priarone M.M., Rey L., Vázquez M., Verweij P.E., Chiller T.M., et al. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Patient with Disseminated Histoplasmosis and HIV—A Case Report from Argentina and Literature Review. J. Fungi. 2020;6:275. doi: 10.3390/jof6040275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

