Impact of COVID-19 at the Ocular Level: A Citation Network Study
- PMID: 33804977
- PMCID: PMC8036864
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071340
Impact of COVID-19 at the Ocular Level: A Citation Network Study
Abstract
Background: The main objective of this study was to use citation networks to analyze the relationship between different publications on the impact of COVID-19 at an ocular level and their authors. Furthermore, the different research areas will be identified, and the most cited publication will be determined.
Materials and methods: The publications were searched within the Web of Science database, using "ocular", "SARS-CoV-2", "ophthalmology", "eyesight", and "COVID-19" as keywords for the period between January 2020 and January 2021. The Citation Network Explorer and the CiteSpace software were used to analyze the different publications.
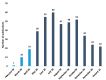
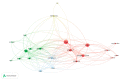
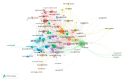
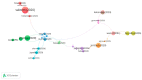
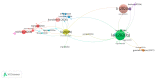
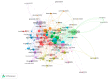
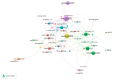
Results: A total of 389 publications with 890 citations generated on the web were found. It must be highlighted that July was the month with the largest number of publications. The most cited ones were "Characteristics of Ocular Findings of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Hubei Province, China" by Wu et al., which was published in May 2020. Three groups covering the different research areas in this field were found using the clustering functions: ocular manifestations, teleophthalmology, and personal protective equipment.
Conclusions: The citation network has shown a comprehensive and objective analysis of the main studies on the impact of COVID-19 in ocular disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 conjunctivitis; SARS-CoV-2; ocular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Influence of Cytokines on Inflammatory Eye Diseases: A Citation Network Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Jan 27;11(3):661. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030661. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35160111 Free PMC article.
-
Citation Network Analysis of the Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 21;17(20):7690. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17207690. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33096796 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Pregnancy: Citation Network Analysis and Evidence Synthesis.JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2022 Mar 3;5(1):e29189. doi: 10.2196/29189. JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2022. PMID: 35044301 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-COV-2 in Ophthalmology: Current Evidence and Standards for Clinical Practice.Acta Med Port. 2020 Sep 1;33(9):593-600. doi: 10.20344/amp.14118. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Acta Med Port. 2020. PMID: 32662416 Review.
-
Ocular surface manifestations of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 5;15(11):e0241661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241661. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33151999 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of research hotspots in COVID-19 genomics based on citespace software: Bibliometric analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 12;12:1060031. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1060031. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36579345 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the information immunology journals transmitted for COVID-19: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 31;13:1035151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035151. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405695 Free PMC article.
-
How Does SARS-CoV-2 Affect Our Eyes-What Have We Learnt So Far about the Ophthalmic Manifestations of COVID-19?J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 13;11(12):3379. doi: 10.3390/jcm11123379. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35743449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Cytokines on Inflammatory Eye Diseases: A Citation Network Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Jan 27;11(3):661. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030661. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35160111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Laboratory Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Suspected Human Cases. World Health Organization. [(accessed on 31 January 2021)];2020 Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331501.
-
- Rolling Updates on Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) [(accessed on 31 January 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

