How Can Malnutrition Affect Autophagy in Chronic Heart Failure? Focus and Perspectives
- PMID: 33805128
- PMCID: PMC8036550
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073332
How Can Malnutrition Affect Autophagy in Chronic Heart Failure? Focus and Perspectives
Abstract
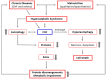
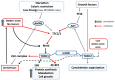
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a disease with important clinical and socio-economic ramifications. Malnutrition and severe alteration of the protein components of the body (protein disarrangements), common conditions in CHF patients, are independent correlates of heart dysfunction, disease progression, and mortality. Autophagy, a prominent occurrence in the heart of patients with advanced CHF, is a self-digestive process that prolongs myocardial cell lifespan by the removal of cytosolic components, such as aging organelles and proteins, and recycles the constituent elements for new protein synthesis. However, in specific conditions, excessive activation of autophagy can lead to the destruction of molecules and organelles essential to cell survival, ultimately leading to organ failure and patient death. In this review, we aim to describe the experimental and clinical evidence supporting a pathophysiological role of nutrition and autophagy in the progression of CHF. The understanding of the mechanisms underlying the interplay between nutrition and autophagy may have important clinical implications by providing molecular targets for innovative therapeutic strategies in CHF patients.
Keywords: amino acids; autophagy; chronic diseases; heart failure; malnutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Tacke M., Ebner N., Boschmann M., Jarius A., Valentova M., Fülster S., Sandek A., Schomburg L., Anker S.D., Doehner W., et al. Resting Energy Expenditure and the Effects of Muscle Wasting in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Results from the Studies Investigating Comorbidities Aggravating Heart Failure (SICA-HF) J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013;14:837–841. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.08.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

