The Impact of Cell-Free DNA Analysis on the Management of Retinoblastoma
- PMID: 33805427
- PMCID: PMC8037190
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071570
The Impact of Cell-Free DNA Analysis on the Management of Retinoblastoma
Abstract
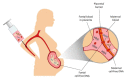
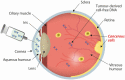
Retinoblastoma is a childhood eye cancer, mainly caused by mutations in the RB1 gene, which can be somatic or constitutional. Unlike many other cancers, tumour biopsies are not performed due to the risk of tumour dissemination. As a result, until recently, somatic genetic analysis was only possible if an affected eye was removed as part of a treatment. Several recent proof of principle studies have demonstrated that the analysis of tumour-derived cell-free DNA, either obtained from ocular fluid or blood plasma, has the potential to advance the diagnosis and influence the prognosis of retinoblastoma patients. It has been shown that a confirmed diagnosis is possible in retinoblastoma patients undergoing conservative treatment. In vivo genetic analysis of retinoblastoma tumours is also now possible, allowing the potential identification of secondary genetic events as prognostic biomarkers. In addition, noninvasive prenatal diagnosis in children at risk of inheriting retinoblastoma has been developed. Here, we review the current literature and discuss the potential impact of cell-free DNA analysis on both the diagnosis and treatment of retinoblastoma patients and their families.
Keywords: cell-free DNA; liquid biopsy; noninvasive prenatal diagnosis; retinoblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lohmann D.R., Gallie B.L. Retinoblastoma. In: Adam M.P., Ardinger H.H., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., Bean L.J., Stephens K., Amemiya A., editors. GeneReviews®. University of Washington; Seattle, WA, USA: 2018.
-
- NHS Conditions: Retinoblastoma. [(accessed on 18 January 2021)]; Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/retinoblastoma/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

