Transcriptional and Non-Transcriptional Activation, Posttranslational Modifications, and Antiviral Functions of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and Viral Antagonism by the SARS-Coronavirus
- PMID: 33805458
- PMCID: PMC8066409
- DOI: 10.3390/v13040575
Transcriptional and Non-Transcriptional Activation, Posttranslational Modifications, and Antiviral Functions of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and Viral Antagonism by the SARS-Coronavirus
Abstract
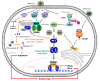
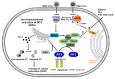
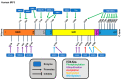
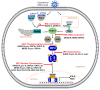
The immune system defends against invading pathogens through the rapid activation of innate immune signaling pathways. Interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) is a key transcription factor activated in response to virus infection and is largely responsible for establishing an antiviral state in the infected host. Studies in Irf3-/- mice have demonstrated the absence of IRF3 imparts a high degree of susceptibility to a wide range of viral infections. Virus infection causes the activation of IRF3 to transcribe type-I interferon (e.g., IFNβ), which is responsible for inducing the interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), which act at specific stages to limit virus replication. In addition to its transcriptional function, IRF3 is also activated to trigger apoptosis of virus-infected cells, as a mechanism to restrict virus spread within the host, in a pathway called RIG-I-like receptor-induced IRF3 mediated pathway of apoptosis (RIPA). These dual functions of IRF3 work in concert to mediate protective immunity against virus infection. These two pathways are activated differentially by the posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of IRF3. Moreover, PTMs regulate not only IRF3 activation and function, but also protein stability. Consequently, many viruses utilize viral proteins or hijack cellular enzymes to inhibit IRF3 functions. This review will describe the PTMs that regulate IRF3's RIPA and transcriptional activities and use coronavirus as a model virus capable of antagonizing IRF3-mediated innate immune responses. A thorough understanding of the cellular control of IRF3 and the mechanisms that viruses use to subvert this system is critical for developing novel therapies for virus-induced pathologies.
Keywords: IRF3; RIPA; SARS-CoV-2; innate antiviral immunity; interferon; posttranslational modifications; viral antagonism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

