A Relationship between NTP and Cell Extract Concentration for Cell-Free Protein Expression
- PMID: 33805612
- PMCID: PMC7999496
- DOI: 10.3390/life11030237
A Relationship between NTP and Cell Extract Concentration for Cell-Free Protein Expression
Abstract
The cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) that synthesizes mRNA and protein from a template DNA has been featured as an important tool to emulate living systems in vitro. However, an obstacle to emulate living cells by CFPS is the loss of activity in the case of usage of high concentration cell extracts. In this study, we found that a high concentration of NTP which inhibits in the case of lower concentration cell extract restored the loss of CFPS activity using high concentration cell extracts. The NTP restoration was independent of the energy regeneration system used, and NTP derivatives also restored the levels of CFPS using a high concentration cell extract. Experiments using dialysis mode of CFPS showed that continuous exchange of small molecule reduced levels of NTP requirement and improved reaction speed of CFPS using the high concentration of cell extract. These findings contribute to the development of a method to understand the condition of living cells by in vitro emulation, and are expected to lead to the achievement of the reconstitution of living cells from biomolecule mixtures.
Keywords: NTP requirement; cell extract; cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS); reconstitution of living cells; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
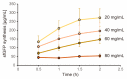


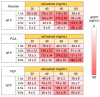

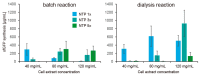
References
-
- Rolf J., Rosenthal K., Lütz S. Application of Cell-Free Protein Synthesis for Faster Biocatalyst Development. Catalysts. 2019;9:190. doi: 10.3390/catal9020190. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

