Chemokine Receptor 5 Antagonism Causes Reduction in Joint Inflammation in a Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model
- PMID: 33805933
- PMCID: PMC8036613
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26071839
Chemokine Receptor 5 Antagonism Causes Reduction in Joint Inflammation in a Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model
Abstract
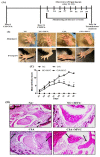
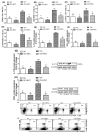
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease mainly affecting the synovial joints. A highly potent antagonist of C-C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5), maraviroc (MVC), plays an essential role in treating several infectious diseases but has not yet been evaluated for its potential effects on RA development. This study focused on evaluating the therapeutic potential of MVC on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1J mice. Following CIA induction, animals were treated intraperitoneally with MVC (50 mg/kg) daily from day 21 until day 35 and evaluated for clinical score and histopathological changes in arthritic inflammation. We further investigated the effect of MVC on Th9 (IL-9, IRF-4, and GATA3) and Th17 (IL-21R, IL-17A, and RORγT) cells, TNF-α, and RANTES in CD8+ T cells in the spleen using flow cytometry. We also assessed the effect of MVC on mRNA and protein levels of IL-9, IL-17A, RORγT, and GATA3 in knee tissues using RT-PCR and western blot analysis. MVC treatment in CIA mice attenuated the clinical and histological severity of inflammatory arthritis, and it substantially decreased IL-9, IRF4, IL-21R, IL-17A, RORγT, TNF-α, and RANTES production but increased GATA3 production in CD8+ T cells. We further observed that MVC treatment decreased IL-9, IL-17A, and RORγt mRNA and protein levels and increased those of GATA3. This study elucidates the capacity of MVC to ameliorate the clinical and histological signs of CIA by reducing pro-inflammatory responses, suggesting that MVC may have novel therapeutic uses in the treatment of RA.
Keywords: CCR5 antagonist; CD8 cells; collagen-induced arthritis; inflammation; maraviroc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Park J.S., Moon S.J., Lim M., Byun J.K., Hwang S.H., Yang S., Kim E.K., Kim S.-M., Lee J., Kwok S., et al. Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Receptor Alpha Ameliorates Autoimmune Arthritis via Inhibiting of Th17 Cells and Osteoclastogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:2270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angelotti F., Parma A., Cafaro G., Capecchi R., Alunno A., Puxeddu I. One year in review 2017: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017;35:368–378. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

