Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan
- PMID: 33806193
- PMCID: PMC8103255
- DOI: 10.3390/dermatopathology8020012
Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan
Abstract
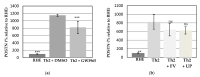
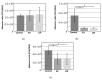
Atopic dermatitis is a multifactorial pathology that includes perturbations of gene expression and increased adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus. Fucoidans are seaweed-derived sulfated fucose-rich polysaccharides that are known to be anti-inflammatory and may inhibit adhesion of pathogens. Fucoidan was assessed for effects on gene expression of an in vitro 3D model of atopic dermatitis. It was also assessed for inhibitory effects on the adhesion of bacteria onto 3D reconstructed skin. Fucoidan significantly altered gene expression in the atopic dermatitis model, and there was a trend to reduce periostin levels. Fucoidan significantly inhibited the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Cutibacterium acnes but did not affect the adhesion of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Fucoidan may be a useful topical agent to assist in the management of atopic dermatitis.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; atopic dermatitis; fucoidan; periostin; reconstructed human epidermis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ah Young Park and Janet Helen Fitton are employees of Marinova Pty Ltd. Maureen Bourtembourg, Aline Chrétien, Roland Hubaux, Céline Lancelot and Michel Salmon are employees of StratiCELL.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Topical application of fucoidan improves atopic dermatitis symptoms in NC/Nga mice.Phytother Res. 2012 Dec;26(12):1898-903. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4658. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 22431003
-
Propionibacterium acnes Abundance Correlates Inversely with Staphylococcus aureus: Data from Atopic Dermatitis Skin Microbiome.Acta Derm Venereol. 2018 Apr 27;98(5):490-495. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2896. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018. PMID: 29379979
-
A topical treatment containing heat-treated Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC 533 reduces Staphylococcus aureus adhesion and induces antimicrobial peptide expression in an in vitro reconstructed human epidermis model.Exp Dermatol. 2018 Apr;27(4):358-365. doi: 10.1111/exd.13504. Exp Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29380443
-
Roles and mechanisms of fucoidan against dermatitis: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 3):135268. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135268. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39233164 Review.
-
The Role of Immune Defects and Colonization of Staphylococcus aureus in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018 May 2;2018:1956403. doi: 10.1155/2018/1956403. eCollection 2018. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29854575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marine cosmetics and the blue bioeconomy: From sourcing to success stories.iScience. 2024 Nov 6;27(12):111339. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111339. eCollection 2024 Dec 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39650733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal Hyaluronan in Barrier Alteration-Related Disease.Cells. 2021 Nov 9;10(11):3096. doi: 10.3390/cells10113096. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of TNFAIP6 Gene in Human Keratinocytes Demonstrates a Role for TSG-6 to Retain Hyaluronan Inside Epidermis.JID Innov. 2021 Aug 23;1(4):100054. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100054. eCollection 2021 Dec. JID Innov. 2021. PMID: 34909750 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic insights into the effects of cosmetics containing complex polysaccharides on the composition of skin microbiota in females.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 1;13:1210724. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1210724. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37593763 Free PMC article.
-
Novel methodologies for host-microbe interactions and microbiome-targeted therapeutics in 3D organotypic skin models.Microbiome. 2023 Oct 17;11(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01668-x. Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37849006 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

