Cytotoxic Mechanism of Sphaerodactylomelol, an Uncommon Bromoditerpene Isolated from Sphaerococcus coronopifolius
- PMID: 33806445
- PMCID: PMC7961984
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26051374
Cytotoxic Mechanism of Sphaerodactylomelol, an Uncommon Bromoditerpene Isolated from Sphaerococcus coronopifolius
Abstract
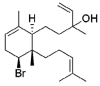
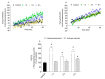
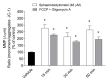
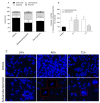
Marine natural products have exhibited uncommon chemical structures with relevant antitumor properties highlighting their potential to inspire the development of new anticancer agents. The goal of this work was to study the antitumor activities of the brominated diterpene sphaerodactylomelol, a rare example of the dactylomelane family. Cytotoxicity (10-100 µM; 24 h) was evaluated on tumor cells (A549, CACO-2, HCT-15, MCF-7, NCI-H226, PC-3, SH-SY5Y, SK-ML-28) and the effects estimated by MTT assay. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) levels and apoptosis biomarkers (membrane translocation of phosphatidylserine, depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential, Caspase-9 activity, and DNA condensation and/or fragmentation) were studied in the breast adenocarcinoma cellular model (MCF-7) and its genotoxicity on mouse fibroblasts (L929). Sphaerodactylomelol displayed an IC50 range between 33.04 and 89.41 µM without selective activity for a specific tumor tissue. The cells' viability decrease was accompanied by an increase on H2O2 production, a depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential and an increase of Caspase-9 activity and DNA fragmentation. However, the DNA damage studies in L929 non-malignant cell line suggested that this compound is not genotoxic for normal fibroblasts. Overall, the results suggest that the cytotoxicity of sphaerodactylomelol seems to be mediated by an increase of H2O2 levels and downstream apoptosis.
Keywords: DNA damage; MCF-7 cells; apoptosis; biological activities; breast cancer; marine natural products; oxidative stress; red algae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Habtetsion T., Ding Z.-C., Pi W., Li T., Lu C., Chen T., Xi C., Spartz H., Liu K., Hao Z., et al. Alteration of Tumor Metabolism by CD4+ T Cells Leads to TNF-α-Dependent Intensification of Oxidative Stress and Tumor Cell Death. Cell Metab. 2018;28:228–242.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.05.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UID/MAR/04292/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- UID/Multi/04046/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- UIDB/04046/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- SAICTPAC/0019/ 2015-LISBOA- 01-0145-FEDER-016405/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BIA-OUT/29250/2017/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

