Sex Education in the Spotlight: What Is Working? Systematic Review
- PMID: 33806507
- PMCID: PMC7967369
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18052555
Sex Education in the Spotlight: What Is Working? Systematic Review
Abstract
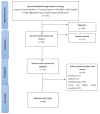
Adolescence, a period of physical, social, cognitive and emotional development, represents a target population for sexual health promotion and education when it comes to achieving the 2030 Agenda goals for sustainable and equitable societies. The aim of this study is to provide an overview of what is known about the dissemination and effectiveness of sex education programs and thereby to inform better public policy making in this area. Methodology: We carried out a systematic review based on international scientific literature, in which only peer-reviewed papers were included. To identify reviews, we carried out an electronic search of the Cochrane Database Reviews, ERIC, Web of Science, PubMed, Medline, Scopus and PsycINFO. This paper provides a narrative review of reviews of the literature from 2015 to 2020. Results: 20 reviews met the inclusion criteria (10 in school settings, 9 using digital platforms and 1 blended learning program): they focused mainly on reducing risk behaviors (e.g., VIH/STIs and unwanted pregnancies), whilst obviating themes such as desire and pleasure, which were not included in outcome evaluations. The reviews with the lowest risk of bias are those carried out in school settings and are the ones that most question the effectiveness of sex education programs. Whilst the reviews of digital platforms and blended learning show greater effectiveness in terms of promoting sexual and reproductive health in adolescents (ASRH), they nevertheless also include greater risks of bias. Conclusion: A more rigorous assessment of the effectiveness of sexual education programs is necessary, especially regarding the opportunities offered by new technologies, which may lead to more cost-effective interventions than with in-person programs. Moreover, blended learning programs offer a promising way forward, as they combine the best of face-to-face and digital interventions, and may provide an excellent tool in the new context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: adolescents; blended learning; digital platforms; review of reviews; school setting; sexual and reproductive health; sexual education.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO The Health of Youth. Geneva 1989. [(accessed on 12 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/pdfs/9241591269_....
-
- WHO Defining Sexual Health Report of a Technical Consultation on Sexual Health, Geneva 2006. [(accessed on 15 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/gender_rights/defining_sex....
-
- UN Agenda 2030 para el Desarrollo Sostenible. [(accessed on 9 April 2020)];2015 Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/es/2015/09/la-asamblea-general...
-
- Blanc M.A., Rojas T.A. Condom use, number of partners and sexual debut in young people in penile-vaginal intercourse, oral sex and anal sex. Rev. Int. 2018;16:8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous