Zearalenone Induces Endothelial Cell Apoptosis through Activation of a Cytosolic Ca2+/ERK1/2/p53/Caspase 3 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33806711
- PMCID: PMC8001463
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13030187
Zearalenone Induces Endothelial Cell Apoptosis through Activation of a Cytosolic Ca2+/ERK1/2/p53/Caspase 3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
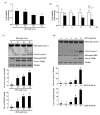
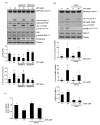
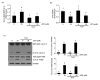
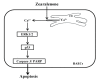
Zearalenone (ZEN) is a mycotoxin that has been reported to damage various types of cells/tissues, yet its effects on endothelial cells (ECs) have never been investigated. Therefore, this study investigates the potential effects of ZEN using bovine aortic ECs (BAECs). In this study, we found that ZEN induced apoptosis of BAECs through increased cleavage of caspase 3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP). ZEN also increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p53, and treatment with the ERK1/2 or p53 inhibitor reversed ZEN-induced EC apoptosis. Transfection of BAECs with small interfering RNA against ERK1/2 or p53 revealed ERK1/2 as an upstream target of p53 in ZEN-stimulated apoptosis. ZEN increased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), yet treatment with the antioxidant did not prevent EC apoptosis. Similarly, blocking of estrogen receptors by specific inhibitors also did not prevent ZEN-induced apoptosis. Finally, chelation of cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) using BAPTA-AM or inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ channel using 2-APB reversed ZEN-induced EC apoptosis, but not by inhibiting ER stress using 4-PBA. Together, our findings demonstrate that ZEN induces EC apoptosis through an ERK1/2/p53/caspase 3 signaling pathway activated by Ca2+ release from the ER, and this pathway is independent of ROS production and estrogen receptor activation.
Keywords: apoptosis; calcium; endothelial cells; mycotoxin; zearalenone.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Belhassen H., Jimenez-Diaz I., Ghali R., Ghorbel H., Molina-Molina J.M., Olea N., Hedili A. Validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of zearalenone, alpha-zearalenol, beta-zearalenol, alpha-zearalanol, be-ta-zearalanol and zearalanone in human urine. J. Chromatogr. B. 2014;962:68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.05.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

