Protein Substitute Requirements of Patients with Phenylketonuria on BH4 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33807079
- PMCID: PMC8004763
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13031040
Protein Substitute Requirements of Patients with Phenylketonuria on BH4 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The traditional treatment for phenylketonuria (PKU) is a phenylalanine (Phe)-restricted diet, supplemented with a Phe-free/low-Phe protein substitute. Pharmaceutical treatment with synthetic tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), an enzyme cofactor, allows a patient subgroup to relax their diet. However, dietary protocols guiding the adjustments of protein equivalent intake from protein substitute with BH4 treatment are lacking. We systematically reviewed protein substitute usage with long-term BH4 therapy. Electronic databases were searched for articles published between January 2000 and March 2020. Eighteen studies (306 PKU patients) were eligible. Meta-analyses demonstrated a significant increase in Phe and natural protein intakes and a significant decrease in protein equivalent intake from protein substitute with cofactor therapy. Protein substitute could be discontinued in 51% of responsive patients, but was still required in 49%, despite improvement in Phe tolerance. Normal growth was maintained, but micronutrient deficiency was observed with BH4 treatment. A systematic protocol to increase natural protein intake while reducing protein substitute dose should be followed to ensure protein and micronutrient requirements are met and sustained. We propose recommendations to guide healthcare professionals when adjusting dietary prescriptions of PKU patients on BH4. Studies investigating new therapeutic options in PKU should systematically collect data on protein substitute and natural protein intakes, as well as other nutritional factors.
Keywords: BH4; PKU; amino acid mixture; hyperphenylalaninemia; medical formula; phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency; protein substitute; sapropterin; tetrahydrobiopterin.
Conflict of interest statement
F.I. and E.K. declare no conflict of interest. A.P. has received an educational grant from Cambrooke Therapeutics and grants from Vitaflo, Danone Nutricia, Merck Serono, Biomarin, and Mevalia to attend scientific meetings. C.R. has received honoraria from Danone Nutricia, MetaX, Schär, Biomarin, and Vitaflo. H.G.-Ö. is a member of the European nutrition expert panel (Biomarin) and she is on the scientific advisory board of Danone Nutricia Metabolics Turkey. R.S. has served on the global medical advisory board for Danone Nutricia and Biomarin. A.M. has received research funding and honoraria from Danone Nutricia, Vitaflo International, Biomarin, MetaX, Applied Pharma Research, and Merck Serono; she is a member of the advisory board for Danone Nutricia, Arla, and Applied Pharma Research. C.M. and M.K. are Danone Nutricia Research employees.
Figures
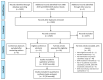

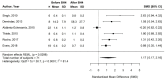

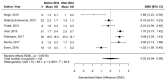
References
-
- Van Wegberg A.M.J., Macdonald A., Ahring K., BãLanger-Quintana A., Blau N., Bosch A.M., Burlina A., Campistol J., Feillet F., Giżewska M., et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017;12:1–56. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0685-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

