Acromio-Humeral Distance Is Associated with Shoulder External Strength in National Elite Badminton Players-A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 33807130
- PMCID: PMC8065938
- DOI: 10.3390/sports9040048
Acromio-Humeral Distance Is Associated with Shoulder External Strength in National Elite Badminton Players-A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Purpose: To examine acromio-humeral distance (AHD) and shoulder isometric strength for external rotation (ER) and internal rotation (IR) in national elite badminton players.
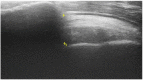
Methods: Seven elite badminton players with asymptomatic shoulders aged 24 ± 4 (mean ± SD) from the Danish national badminton team were investigated. Shoulder AHD, isometric strength in ER and IR were bilaterally assessed with ultrasonography and a hand-held dynamometer (HHD).
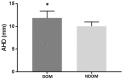
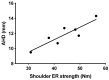
Results: AHD was greater on the dominant vs. the nondominant side (p = 0.018). Moreover, IR strength was greater on the dominant side vs. the nondominant side (p = 0.041). Furthermore, AHD and ER strength were highly correlated on the dominant side (p = 0.007, r = 0.900). A correlation was also shown between AHD and the ER/IR strength ratio on the dominant side (p = 0.033, r = 0.793).
Conclusion: This preliminary study demonstrates that shoulder ER strength is strongly associated with AHD size, largely reflecting supraspinatus tendon-muscle hypertrophy as a result of sport-specific adaptation in national elite badminton players with asymptomatic shoulders. These novel data also suggest that habitual loading of the shoulder improves the supraspinatus tendon size, which may lower the mechanical stress and potentially reduce the risk of injury. This warrants strengthening the shoulder external rotators as a potential strategy to reduce the risk of future shoulder injury.
Keywords: overhead athlete; shoulder rotational strength; sport-specific adaptations; supraspinatus tendon hypertrophy; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Urwin M., Symmons D., Allison T., Brammah T., Busby H., Roxby M., Simmons A.W.G. Estimating the burden of muskuloskeletal disorders in the community: The comparative prevalence of symptoms at different anatomical sites, and the relation to social deprivation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998;57:649–655. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.11.649. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

