Functional and Phylogenetic Diversity of BSH and PVA Enzymes
- PMID: 33807488
- PMCID: PMC8066178
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9040732
Functional and Phylogenetic Diversity of BSH and PVA Enzymes
Abstract
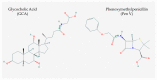
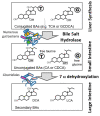
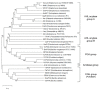
Bile salt hydrolase (BSH) and penicillin V acylase (PVA) are related enzymes that are classified as choloylglycine hydrolases (CGH). BSH enzymes have attracted significant interest for their ability to modulate the composition of the bile acid pool, alter bile acid signaling events mediated by the host bile acid receptors FXR and TGR5 and influence cholesterol homeostasis in the host, while PVA enzymes have been widely utilised in an industrial capacity in the production of semi-synthetic antibiotics. The similarities between BSH and PVA enzymes suggest common evolution of these enzymes and shared mechanisms for substrate binding and catalysis. Here, we compare BSH and PVA through analysis of the distribution, phylogeny and biochemistry of these microbial enzymes. The development of new annotation approaches based upon functional enzyme analyses and the potential implications of BSH enzymes for host health are discussed.
Keywords: FXR; TGR5; bile acid; bile salt hydrolase; cholesterol; microbiome; penicillin V acylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

