Vector Competence of Florida Culicoides insignis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) for Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype-2
- PMID: 33807536
- PMCID: PMC7998304
- DOI: 10.3390/v13030410
Vector Competence of Florida Culicoides insignis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) for Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype-2
Abstract
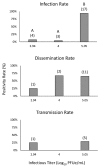
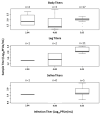
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV; family Reoviridae, genus Orbivirus) is an arthropod-borne virus of ungulates, primarily white-tailed deer in North America. Culicoides sonorensis, the only confirmed North American vector of EHDV, is rarely collected from Florida despite annual virus outbreaks. Culicoides insignis is an abundant species in Florida and is also a confirmed vector of the closely related Bluetongue virus. In this study, oral challenge of C. insignis was performed to determine vector competence for EHDV serotype-2. Field-collected female midges were provided bovine blood spiked with three different titers of EHDV-2 (5.05, 4.00, or 2.94 log10PFUe/mL). After an incubation period of 10 days or after death, bodies and legs were collected. Saliva was collected daily from all females from 3 days post feeding until their death using honey card assays. All samples were tested for EHDV RNA using RT-qPCR. Our results suggest that C. insignis is a weakly competent vector of EHDV-2 that can support a transmissible infection when it ingests a high virus titer (29% of midges had virus positive saliva when infected at 5.05 log10PFUe/mL), but not lower virus titers. Nevertheless, due to the high density of this species, particularly in peninsular Florida, it is likely that C. insignis plays a role in the transmission of EHDV-2.
Keywords: Orbivirus; Reoviridae; arboviruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ruder M.G., Lysyk T.J., Stallknecht D.E., Foil L.D., Johnson D.J., Chase C.C., Dargatz D.A., Gibbs E.P.J. Transmission and epidemiology of Bluetongue and Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease in North America: Current perspectives, research gaps, and future directions. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015;15:348–363. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2014.1703. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

