Underwater Object Recognition Using Point-Features, Bayesian Estimation and Semantic Information
- PMID: 33807708
- PMCID: PMC7961582
- DOI: 10.3390/s21051807
Underwater Object Recognition Using Point-Features, Bayesian Estimation and Semantic Information
Abstract
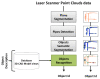
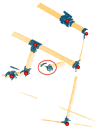
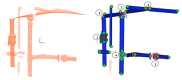
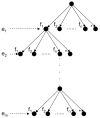
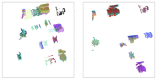
This paper proposes a 3D object recognition method for non-coloured point clouds using point features. The method is intended for application scenarios such as Inspection, Maintenance and Repair (IMR) of industrial sub-sea structures composed of pipes and connecting objects (such as valves, elbows and R-Tee connectors). The recognition algorithm uses a database of partial views of the objects, stored as point clouds, which is available a priori. The recognition pipeline has 5 stages: (1) Plane segmentation, (2) Pipe detection, (3) Semantic Object-segmentation and detection, (4) Feature based Object Recognition and (5) Bayesian estimation. To apply the Bayesian estimation, an object tracking method based on a new Interdistance Joint Compatibility Branch and Bound (IJCBB) algorithm is proposed. The paper studies the recognition performance depending on: (1) the point feature descriptor used, (2) the use (or not) of Bayesian estimation and (3) the inclusion of semantic information about the objects connections. The methods are tested using an experimental dataset containing laser scans and Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) navigation data. The best results are obtained using the Clustered Viewpoint Feature Histogram (CVFH) descriptor, achieving recognition rates of 51.2%, 68.6% and 90%, respectively, clearly showing the advantages of using the Bayesian estimation (18% increase) and the inclusion of semantic information (21% further increase).
Keywords: 3D object recognition; AUV; Bayesian probabilities; JCBB; autonomous manipulation; global descriptors; inspection; laser scanner; maintenance and repair; multi-object tracking; pipeline detection; point clouds; semantic information; semantic segmentation; underwater environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


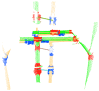




Similar articles
-
Semantic Mapping for Autonomous Subsea Intervention.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;21(20):6740. doi: 10.3390/s21206740. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34695951 Free PMC article.
-
3D Object Recognition Based on Point Clouds in Underwater Environment with Global Descriptors: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 14;19(20):4451. doi: 10.3390/s19204451. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31615081 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Object Recognition and Registration for Robotic Grasping Systems Using a Modified Viewpoint Feature Histogram.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Nov 23;16(11):1969. doi: 10.3390/s16111969. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27886080 Free PMC article.
-
State of the Art of Underwater Active Optical 3D Scanners.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Nov 25;19(23):5161. doi: 10.3390/s19235161. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31775354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inspection and maintenance of industrial infrastructure with autonomous underwater robots.Front Robot AI. 2023 Aug 25;10:1240276. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2023.1240276. eCollection 2023. Front Robot AI. 2023. PMID: 37692529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of Underwater Materials of Bionic and Natural Fishes Based on Blue-Green Light Reflection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 7;22(24):9600. doi: 10.3390/s22249600. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559971 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Immersion Scanning Technique: A Scalable Low-Cost Solution for 3D Scanning Using Water-Based Fluid.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;23(6):3214. doi: 10.3390/s23063214. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36991924 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Pipe and Valve Characterisation and Mapping for Autonomous Underwater Intervention Tasks.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;22(21):8141. doi: 10.3390/s22218141. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365839 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic Mapping for Autonomous Subsea Intervention.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;21(20):6740. doi: 10.3390/s21206740. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34695951 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid Bi-LSTM and RBM approach for advanced underwater object detection.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 22;19(11):e0313708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313708. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39576806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu Q., Chen L., Li Q., Li M., Nüchter A., Wang J. 3d lidar point cloud based intersection recognition for autonomous driving; Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium; Madrid, Spain. 3–7 June 2012; pp. 456–461.
-
- Li D., Wang H., Liu N., Wang X., Xu J. 3D Object Recognition and Pose Estimation From Point Cloud Using Stably Observed Point Pair Feature. IEEE Access. 2020;8:44335–44345. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978255. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

