Influence of Teacher and Family Support on University Student Motivation and Engagement
- PMID: 33807813
- PMCID: PMC7967384
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18052606
Influence of Teacher and Family Support on University Student Motivation and Engagement
Abstract
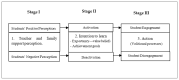
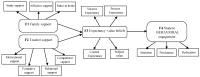
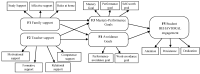
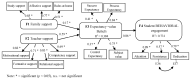
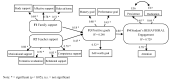
Although many studies endorse the notion that the way students perceive support influences their engagement, very few have explored the possible mediator role of intention to learn between these variables. The present work provides new evidence to the existing literature because it analyses the work of intention to learn (measured with expectancy-value beliefs and achievement goals) as a mediating motivational variable in the relation between university students' external support (teacher and family) and their engagement. The Educational Situation Quality Model (MOCSE, its acronym in Spanish) has employed as a theoretical framework to perform this analysis. A sample of 267 Spanish university students completed the questionnaires employed to measure the considered variables at three times. They answered teacher and family support scales when the course began (time 1), intention to learn scales halfway through the course (time 2), and engagement scales when the course ended (time 3). The obtained structural equation models showed a positive and significant effect for teacher and family support on the considered motivational variables (expectancy-value beliefs and achievement goals) and these, in turn, on student behavioral engagement. These results allow us to point out a series of recommendations for university teachers to improve their students' involvement in their learning process.
Keywords: achievement goals; expectancy beliefs; family support; student engagement; teaching support; value beliefs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Maleki C., Demaray M. What type of support do they need? Investigating student adjustment as related to emotional, informational, appraisal, and instrumental support. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2003;18:231–252. doi: 10.1521/scpq.18.3.231.22576. - DOI
-
- Katz I., Kaplan A., Gueta G. Students’ needs, teachers’ support, and motivation for doing homework: A cross-sectional study. J. Exp. Educ. 2009;78:246–267. doi: 10.1080/00220970903292868. - DOI
-
- Reyes M.R., Brackett M.A., Rivers S.E., White M., Salovey P. Classroom emotional climate, student engagement, and academic achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2012;104:700–712. doi: 10.1037/a0027268. - DOI
-
- Sharma G. Teacher support as determinant of academic achievement. J. Educ. Res. 2016;2:1–9.
-
- Jelas Z.M., Azman N., Zulnaidi H., Ahmad N.A. Learning support and academic achievement among Malaysian adolescents: The mediating role of student engagement. Learn. Environ. Res. 2016;19:221–240. doi: 10.1007/s10984-015-9202-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

