Evaluation of a Lyophilized CRISPR-Cas12 Assay for a Sensitive, Specific, and Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33807908
- PMCID: PMC7998296
- DOI: 10.3390/v13030420
Evaluation of a Lyophilized CRISPR-Cas12 Assay for a Sensitive, Specific, and Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
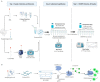
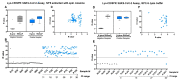
We evaluated a lyophilized CRISPR-Cas12 assay for SARS-CoV-2 detection (Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 kit) based on reverse transcription, isothermal amplification, and CRISPR-Cas12 reaction. From a total of 210 RNA samples extracted from nasopharyngeal swabs using spin columns, the Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 kit detected 105/105 (100%; 95% confidence interval (CI): 96.55-100) positive samples and 104/105 (99.05%; 95% CI: 94.81-99.97) negative samples that were previously tested using commercial RT-qPCR. The estimated overall Kappa index was 0.991, reflecting an almost perfect concordance level between the two diagnostic tests. An initial validation test was also performed on 30 nasopharyngeal samples collected in lysis buffer, in which the Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 kit detected 20/21 (95.24%; 95% CI: 76.18-99.88) positive samples and 9/9 (100%; 95% CI: 66.37-100) negative samples. The estimated Kappa index was 0.923, indicating a strong concordance between the test procedures. The Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 kit was suitable for detecting a wide range of RT-qPCR-positive samples (cycle threshold range: 11.45-36.90) and dilutions of heat-inactivated virus (range: 2.5-100 copies/µL); no cross-reaction was observed with the other respiratory pathogens tested. We demonstrated that the performance of the Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 kit was similar to that of commercial RT-qPCR, as the former was highly sensitive and specific, timesaving (1.5 h), inexpensive, and did not require sophisticated equipment. The use of this kit would reduce the time taken for diagnosis and facilitate molecular diagnosis in low-resource laboratories.
Keywords: COVID-19; CRISPR; SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; fluorescence detection; lysis buffer.
Conflict of interest statement
L.A.C; G.D.R; J.L.; I.P. (Ivana Parcerisa); A.P., M.E.L.; F.P.B. and C.A.G. are members of CASPR Biotech. I.P. (Ivana Primost); S.V.; D.I.A.; C.O.P.; A.R.; M.B. and DNM declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection: A Multicenter Comparison Between Standard Quantitative Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction and CRISPR-Based DETECTR.J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 3;223(2):206-213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa641. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33535237 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Novel COVID-19 nsp8 One-Tube RT-LAMP-CRISPR Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0196222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01962-22. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36445095 Free PMC article.
-
iSCAN: An RT-LAMP-coupled CRISPR-Cas12 module for rapid, sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2.Virus Res. 2020 Oct 15;288:198129. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198129. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32822689 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the Cepheid Xpert Xpress and the Abbott ID NOW assay for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2021 Jul;93(7):4523-4531. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26994. Epub 2021 May 3. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33913533 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-based tools: Alternative methods for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Clin Biochem. 2021 Mar;89:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.12.011. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Clin Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33428900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of CRISPR-Based Assays for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Yonsei Med J. 2022 May;63(5):480-489. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.5.480. Yonsei Med J. 2022. PMID: 35512751 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive, Specific, and Rapid Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Using the ERA/CRISPR-Cas12a Dual System.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 13;13:811768. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.811768. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35633705 Free PMC article.
-
Inconsistent treatments of the kinetics of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) impair assessment of its diagnostic potential.QRB Discov. 2022 Jun 28;3:e9. doi: 10.1017/qrd.2022.7. eCollection 2022. QRB Discov. 2022. PMID: 37529278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) to diagnose COVID-19, a meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2022 Apr;165:105498. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105498. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35341958 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and sensitive on-site genetic diagnostics of pest fruit flies using CRISPR-Cas12a.Pest Manag Sci. 2023 Jan;79(1):68-75. doi: 10.1002/ps.7173. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Pest Manag Sci. 2023. PMID: 36073293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., de Groot R.J., Drosten C., Gulyaeva A.A., Haagmans B.L., Lauber C., Leontovich A.M., Neuman B.W., et al. The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020;5:536–544. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Situation Reports. [(accessed on 13 February 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
-
- CDC Information for Laboratories about Coronavirus (COVID-19) [(accessed on 14 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/virus-requests.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

