Functional Dysregulations in CA1 Hippocampal Networks of a 3-Hit Mouse Model of Schizophrenia
- PMID: 33807989
- PMCID: PMC7961987
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052644
Functional Dysregulations in CA1 Hippocampal Networks of a 3-Hit Mouse Model of Schizophrenia
Abstract
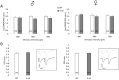
For a better translation from treatment designs of schizophrenia to clinical efficiency, there is a crucial need to refine preclinical animal models. In order to consider the multifactorial nature of the disorder, a new mouse model associating three factors (genetic susceptibility-partial deletion of the MAP6 gene, early-life stress-maternal separation, and pharmacological treatment-chronic Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol during adolescence) has recently been described. While this model depicts a schizophrenia-like phenotype, the neurobiological correlates remain unknown. Synaptic transmission and functional plasticity of the CA1 hippocampal region of male and female 3-hit mice were therefore investigated using electrophysiological recordings on the hippocampus slice. While basal excitatory transmission remained unaffected, NMDA receptor (NMDAr)-mediated long-term potentiation (LTP) triggered by theta-burst (TBS) but not by high-frequency (HFS) stimulation was impaired in 3-hit mice. Isolated NMDAr activation was not affected or even increased in female 3-hit mice, revealing a sexual dimorphism. Considering that the regulation of LTP is more prone to inhibitory tone if triggered by TBS than by HFS, the weaker potentiation in 3-hit mice suggests a deficiency of intrinsic GABA regulatory mechanisms. Indeed, NMDAr activation was increased by GABAA receptor blockade in wild-type but not in 3-hit mice. This electrophysiological study highlights dysregulations of functional properties and plasticity in hippocampal networks of 3-hit mice, one of the mechanisms suspected to contribute to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. It also shows differences between males and females, supporting the sexual dimorphism observed in the disorder. Combined with the previously reported study, the present data reinforce the face validity of the 3-hit model that will help to consider new therapeutic strategies for psychosis.
Keywords: NMDA receptor; functional plasticity; hippocampus; long term potentiation; psychiatric disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bouet V., Boulouard M., Freret T. Advances in Schizophrenia Research. Normandie University; Caen, France: 2016. [(accessed on 21 September 2020)]. Animal models of schizophrenia: An update. Available online: www.openaccessebooks.com.
-
- Ellenbroek B.A., Riva M.A. Early maternal deprivation as an animal model for schizophrenia. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2003;3:297–302. doi: 10.1016/S1566-2772(03)00090-2. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

