Changes in Serum MicroRNAs after Anti-IL-5 Biological Treatment of Severe Asthma
- PMID: 33808110
- PMCID: PMC8038078
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073558
Changes in Serum MicroRNAs after Anti-IL-5 Biological Treatment of Severe Asthma
Abstract
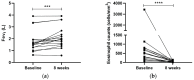
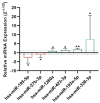
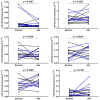
There is currently enough evidence to think that miRNAs play a role in several key points in asthma, including diagnosis, severity of the disease, and response to treatment. Cells release different types of lipid double-membrane vesicles into the extracellular microenvironment, including exosomes, which function as very important elements in intercellular communication. They are capable of distributing genetic material, mRNA, mitochondrial DNA, and microRNAs (miRNAs). Serum miRNA screening was performed in order to analyze possible changes in serum miRNAs in 10 patients treated with reslizumab and 6 patients with mepolizumab after 8 weeks of treatment. The expression of miR-338-3p was altered after treatment (p < 0.05), although no significant differences between reslizumab and mepolizumab were found. Bioinformatic analysis showed that miR-338-3p regulates important pathways in asthma, such as the MAPK and TGF-β signaling pathways and the biosynthesis/degradation of glucans (p < 0.05). However, it did not correlate with an improvement in lung function. MiRNA-338-3p could be used as a biomarker of early response to reslizumab and mepolizumab in severe eosinophilic asthmatic patients. In fact, this miRNA could be involved in airway remodeling, targeting genes related to MAPK and TGF-β signaling pathways.
Keywords: anti-IL5 biologics; biomarkers; mepolizumab; microRNAs; reslizumab; severe asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.R. has received pay for lectures from Astra-Zéneca, Chiesi, Merck, GSK, Allergy Therapeutics, Novartis, ALK, TEVA, and Shire. J.A.C. has received pay for lectures from Astra Zeneca. J.S. reports having served as a consultant to Thermofisher, MEDA, Novartis, Sanofi, Leti, Faes Farma, Mundipharma, and GSK and having been paid lecture fees by Novartis, GSK, Stallergenes, Leti, and Faes Farma as well as having received grant support for research from Thermofisher, Sanofi, and ALK. V.d.P. reports having served as a consultant to Astra Zeneca and GSK and having been paid lecture fees by Astra Zeneca and GSK. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe eosinophilic asthma: from the pathogenic role of interleukin-5 to the therapeutic action of mepolizumab.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Oct 30;11:3137-3144. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S150656. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 29133975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for the efficacy and safety of anti-interleukin-5 treatment in the management of refractory eosinophilic asthma.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):135-45. doi: 10.1177/1753465815581279. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015. PMID: 25900924 Review.
-
Reslizumab in the treatment of severe eosinophilic asthma: an update.Immunotherapy. 2018 Jun;10(8):695-698. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0176. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Immunotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29554826 Review.
-
Mepolizumab: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2015 Dec;75(18):2163-9. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0513-8. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26603873 Review.
-
Antibodies targeting the interleukin-5 signaling pathway used as add-on therapy for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: a review of the mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety of the subcutaneously administered agents, mepolizumab and benralizumab.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Apr;14(4):353-365. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2020.1718495. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 31958239 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA DHTKD1 targets miR‑338‑3p/ETS1 axis to regulate the inflammatory response in human bronchial epithelial cells.Exp Ther Med. 2023 May 15;26(1):316. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12015. eCollection 2023 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37273760 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic Asthma: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Horizons.Cells. 2024 Feb 23;13(5):384. doi: 10.3390/cells13050384. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs as Modern Biomarkers in Asthma Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 15;24(14):11499. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411499. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis Factors as Emerging Circulating Biomarkers in Asthma.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2025 Jan;17(1):22-31. doi: 10.4168/aair.2025.17.1.22. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 39895600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of anti-IL-5/5Rα biologics in severe asthma in real-world studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.ERJ Open Res. 2025 Mar 24;11(2):00625-2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00625-2024. eCollection 2025 Mar. ERJ Open Res. 2025. PMID: 40129552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castro M., Zangrilli J., Wechsler M.E., Bateman E.D., Brusselle G.G., Bardin P., Murphy K., Maspero J.F., O’Brien C., Korn S. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: Results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015;3:355–366. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00042-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

