Growth and Viability of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Display Different Sensitivities to Isoform-Specific Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 33808215
- PMCID: PMC8036316
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073567
Growth and Viability of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Display Different Sensitivities to Isoform-Specific Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
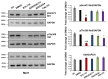
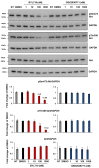
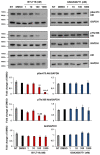
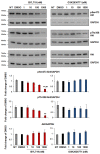
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (cSCCs) account for about 20% of keratinocyte carcinomas, the most common cancer in the UK. Therapeutic options for cSCC patients who develop metastasis are limited and a better understanding of the biochemical pathways involved in cSCC development/progression is crucial to identify novel therapeutic targets. Evidence indicates that the phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks)/Akt pathway plays an important role, in particular in advanced cSCC. Questions remain of whether all four PI3K isoforms able to activate Akt are involved and whether selective inhibition of specific isoform(s) might represent a more targeted strategy. Here we determined the sensitivity of four patient-derived cSCC cell lines to isoform-specific PI3K inhibitors to start investigating their potential therapeutic value in cSCC. Parallel experiments were performed in immortalized keratinocyte cell lines. We observed that pan PI3Ks inhibition reduced the growth/viability of all tested cell lines, confirming the crucial role of this pathway. Selective inhibition of the PI3K isoform p110α reduced growth/viability of keratinocytes and of two cSCC cell lines while affecting the other two only slightly. Importantly, p110α inhibition reduced Akt phosphorylation in all cSCC cell lines. These data indicate that growth and viability of the investigated cSCC cells display differential sensitivity to isoform-specific PI3K inhibitors.
Keywords: BYL719; cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; isoform-specific PI3K inhibitors; mTOR; phosphoinositide 3-kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Mutational and Phenotypic Characterization of New Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Reveal Novel Drug Susceptibilities.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 15;21(24):9536. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249536. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33333825 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse mechanisms activate the PI 3-kinase/mTOR pathway in melanomas: implications for the use of PI 3-kinase inhibitors to overcome resistance to inhibitors of BRAF and MEK.BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 6;21(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07826-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33549048 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00520 prevents the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by downregulating EGFR.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Feb;132(4):454-465. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000070. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30707166 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway: an emerging treatment strategy for squamous cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Sep;40(8):980-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037117 Review.
-
Picking the point of inhibition: a comparative review of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(5):1021-31. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0639. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24748656 Review.
Cited by
-
PIK Your Poison: The Effects of Combining PI3K and CDK Inhibitors against Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;16(2):370. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020370. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254859 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: PIK3CA somatic mutation leading to Klippel Trenaunay Syndrome and multiple tumors.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 17;14:1213283. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1213283. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37662840 Free PMC article.
-
Arctigenin inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 27;19(9):e0308947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308947. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39331595 Free PMC article.
-
KIFC3 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 22;13:848926. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848926. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35812733 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-mRNAs co-expression network identifies potential lncRNA biomarkers in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Genomics. 2022 Apr 7;23(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08481-0. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35392800 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

