Biomimetic Chromatographic Studies Combined with the Computational Approach to Investigate the Ability of Triterpenoid Saponins of Plant Origin to Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 33808219
- PMCID: PMC8037809
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073573
Biomimetic Chromatographic Studies Combined with the Computational Approach to Investigate the Ability of Triterpenoid Saponins of Plant Origin to Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
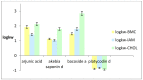
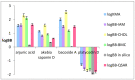
Biomimetic (non-cell based in vitro) and computational (in silico) studies are commonly used as screening tests in laboratory practice in the first stages of an experiment on biologically active compounds (potential drugs) and constitute an important step in the research on the drug design process. The main aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of triterpenoid saponins of plant origin to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) using both computational methods, including QSAR methodology, and biomimetic chromatographic methods, i.e., High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Immobilized Artificial Membrane (IAM) and cholesterol (CHOL) stationary phases, as well as Bio-partitioning Micellar Chromatography (BMC). The tested compounds were as follows: arjunic acid (Terminalia arjuna), akebia saponin D (Akebia quinata), bacoside A (Bacopa monnieri) and platycodin D (Platycodon grandiflorum). The pharmacokinetic BBB parameters calculated in silico show that three of the four substances, i.e., arjunic acid, akebia saponin D, and bacoside A exhibit similar values of brain/plasma equilibration rate expressed as logPSFubrain (the average logPSFubrain: -5.03), whereas the logPSFubrain value for platycodin D is -9.0. Platycodin D also shows the highest value of the unbound fraction in the brain obtained using the examined compounds (0.98). In these studies, it was found out for the first time that the logarithm of the analyte-micelle association constant (logKMA) calculated based on Foley's equation can describe the passage of substances through the BBB. The most similar logBB values were obtained for hydrophilic platycodin D, applying both biomimetic and computational methods. All of the obtained logBB values and physicochemical parameters of the molecule indicate that platycodin D does not cross the BBB (the average logBB: -1.681), even though the in silico estimated value of the fraction unbound in plasma is relatively high (0.52). As far as it is known, this is the first paper that shows the applicability of biomimetic chromatographic methods in predicting the penetration of triterpenoid saponins through the BBB.
Keywords: IAM stationary phase; Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR); biomimetic studies; computational studies; micellar liquid chromatography; triterpenoid saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of biopartitioning micellar chromatography and immobilized artificial membrane column for in silico and in vitro determination of blood-brain barrier penetration of phenols.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Apr 19;1286:127-36. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.071. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23506703
-
In Silico Studies on Triterpenoid Saponins Permeation through the Blood-Brain Barrier Combined with Postmortem Research on the Brain Tissues of Mice Affected by Astragaloside IV Administration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 5;21(7):2534. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072534. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32260588 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of Bacoside A Aglycones and Its Derivatives as the Constituents Responsible for the Cognitive Effects of Bacopa monnieri.PLoS One. 2015 May 12;10(5):e0126565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126565. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25965066 Free PMC article.
-
Insights Into the Molecular Aspects of Neuroprotective Bacoside A and Bacopaside I.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(5):438-446. doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180419123022. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29676230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Killing cancer with platycodin D through multiple mechanisms.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Mar;20(3):389-402. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12749. Epub 2015 Dec 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26648178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitory Potential of the Oleanane-Type Triterpenes and Their Glycosides.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 6;13(9):1357. doi: 10.3390/biom13091357. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759757 Free PMC article.
-
Akebia saponin D protects hippocampal neurogenesis from microglia-mediated inflammation and ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 30;13:927419. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.927419. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36110522 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Investigation of Leaves of Eriobotrya japonica: Antioxidant, Enzyme Inhibition, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 29;14(4):413. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040413. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298661 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic separations in chemistry and life sciences.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 Feb 4;192(3):133. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-06980-x. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39904888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of Interactions between Saponin Biosurfactant and Model Biological Membranes: Phospholipid Monolayers and Liposomes.Molecules. 2023 Feb 18;28(4):1965. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041965. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Dementia: A Public Health Priority. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012. World Health Organization and Alzheimer’s Disease International Report.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials