Fetal High-Density Lipoproteins: Current Knowledge on Particle Metabolism, Composition and Function in Health and Disease
- PMID: 33808220
- PMCID: PMC8067099
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9040349
Fetal High-Density Lipoproteins: Current Knowledge on Particle Metabolism, Composition and Function in Health and Disease
Abstract
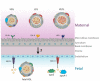
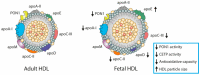
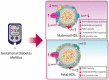
Cholesterol and other lipids carried by lipoproteins play an indispensable role in fetal development. Recent evidence suggests that maternally derived high-density lipoprotein (HDL) differs from fetal HDL with respect to its proteome, size, and function. Compared to the HDL of adults, fetal HDL is the major carrier of cholesterol and has a unique composition that implies other physiological functions. Fetal HDL is enriched in apolipoprotein E, which binds with high affinity to the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Thus, it appears that a primary function of fetal HDL is the transport of cholesterol to tissues as is accomplished by low-density lipoproteins in adults. The fetal HDL-associated bioactive sphingolipid sphingosine-1-phosphate shows strong vasoprotective effects at the fetoplacental vasculature. Moreover, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 carried by fetal-HDL exerts anti-oxidative and athero-protective functions on the fetoplacental endothelium. Notably, the mass and activity of HDL-associated paraoxonase 1 are about 5-fold lower in the fetus, accompanied by an attenuation of anti-oxidative activity of fetal HDL. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity is reduced in fetal circulation despite similar amounts of the enzyme in maternal and fetal serum. This review summarizes the current knowledge on fetal HDL as a potential vasoprotective lipoprotein during fetal development. We also provide an overview of whether and how the protective functionalities of HDL are impaired in pregnancy-related syndromes such as pre-eclampsia or gestational diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: HDL; LpPLA2; fetal development; gestational diabetes mellitus; preeclampsia; pregnancy; sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct composition of human fetal HDL attenuates its anti-oxidative capacity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1831(4):737-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.12.015. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23321267
-
Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus increases placental and foetal lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2 which might exert protective functions against oxidative stress.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 3;7(1):12628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13051-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28974763 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal and maternal lipoprotein metabolism in human pregnancy complicated by type I diabetes mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 May;83(5):1736-41. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.5.4783. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. PMID: 9589684
-
Alterations in high-density lipoprotein metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus: role of lipolytic enzymes, lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and lipid transfer proteins.Eur J Clin Invest. 2003 Dec;33(12):1051-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2003.01263.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14636288 Review.
-
Role of lipases, lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in abnormal high density lipoprotein metabolism in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Clin Lab. 2003;49(11-12):601-13. Clin Lab. 2003. PMID: 14651331 Review.
Cited by
-
Foetal lipoprotein oxidation and preeclampsia.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Jun 4;21(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01663-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 35658865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total Outflow of High-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesteryl Esters from Plasma Is Decreased in a Model of 3/4 Renal Mass Reduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 4;24(23):17090. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317090. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069414 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior with Maternal and Cord Blood Anti-Oxidative Capacity and HDL Functionality: Findings of DALI Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;12(4):827. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040827. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107203 Free PMC article.
-
High-Density Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Disease: The Good, the Bad, and the Future II.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 7;10(3):620. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030620. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327422 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Underweight on Cord Blood Metabolome: An Analysis of the Population-Based Survey of Neonates in Pomerania (SNiP).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7552. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147552. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062795 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

