A Model-Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analysis of the Combination of Amoxicillin and Monophosphoryl Lipid A Against S. pneumoniae in Mice
- PMID: 33808396
- PMCID: PMC8065677
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040469
A Model-Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analysis of the Combination of Amoxicillin and Monophosphoryl Lipid A Against S. pneumoniae in Mice
Abstract
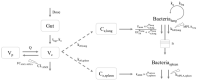
Combining amoxicillin with the immunostimulatory toll-like receptor 4 agonist monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA) represents an innovative approach for enhancing antibacterial treatment success. Exploiting pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data from an infection model of Streptococcus pneumoniae infected mice, we aimed to evaluate the preclinical exposure-response relationship of amoxicillin with MPLA coadministration and establish a link to survival. Antibiotic serum concentrations, bacterial numbers in lung and spleen and survival data of mice being untreated or treated with amoxicillin (four dose levels), MPLA, or their combination were analyzed by nonlinear mixed-effects modelling and time-to-event analysis using NONMEM® to characterize these treatment regimens. On top of a pharmacokinetic interaction, regarding the pharmacodynamic effects the combined treatment was superior to both monotherapies: The amoxicillin efficacy at highest dose was increased by a bacterial reduction of 1.74 log10 CFU/lung after 36 h and survival was increased 1.35-fold to 90.3% after 14 days both compared to amoxicillin alone. The developed pharmacometric pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic disease-treatment-survival models provided quantitative insights into a novel treatment option against pneumonia revealing a pharmacokinetic interaction and enhanced activity of amoxicillin and the immune system stimulator MPLA in combination. Further development of this drug combination flanked with pharmacometrics towards the clinical setting seems promising.
Keywords: MPLA; amoxicillin; immunomodulation; murine model; pharmacometric PK/PD modelling; time-to-event modelling.
Conflict of interest statement
CK reports research grants from an industry consortium (AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Grünenthal GmbH, Astra Zeneca, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Merck KGaA and SANOFI) for the PharMetrX program, the Innovative Medicines Initiative-Joint Undertaking (‘DDMoRe’), Diurnal Ltd. and the European Commission within the Horizon 2020 framework programme (“FAIR”), all outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2016 Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators Estimates of global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoeal diseases: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018;18:1191–1210. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30276-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines, 20th ed. [(accessed on 13 April 2020)];2017 Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/expert-committee-on-selection-and-use-of-esse....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

