Pulsed Dose Rate Brachytherapy of Lip Carcinoma: Clinical Outcome and Quality of Life Analysis
- PMID: 33808535
- PMCID: PMC8003123
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061387
Pulsed Dose Rate Brachytherapy of Lip Carcinoma: Clinical Outcome and Quality of Life Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Lip carcinoma represents one of the most common types of head and neck cancer. Brachytherapy is a highly effective therapeutic option for all stages of lip cancers. We report our experience of pulsed dose rate brachytherapy (PDR) as treatment of lip carcinoma.
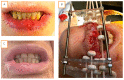
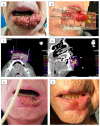
Methods and materials: this retrospective single center study included all consecutive patients treated for a lip PDR brachytherapy in our institution from 2010 to 2019. The toxicities and outcomes of the patients were reported, and a retrospective quality of life assessment was conducted by phone interviews (FACT H&N).
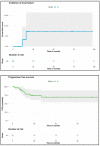
Results: From October 2010 to December 2019, 38 patients were treated in our institution for a lip carcinoma by PDR brachytherapy. The median age was 73, and the majority of patients presented T1-T2 tumors (79%). The median total dose was 70.14 Gy (range: 60-85 Gy). With a mean follow-up of 35.4 months, two patients (5.6%) presented local failure, and seven patients (19%) had lymph node progression. The Kaplan-Meier estimated probability of local failure was 7.2% (95% CI: 0.84-1) at two and four years. All patients encountered radiomucitis grade II or higher. The rate of late toxicities was low: three patients (8.3%) had grade II fibrosis, and one patient had grade II chronic pain. All patients would highly recommend the treatment. The median FACT H&N total score was 127 out of 148, and the median FACT H&N Trial Outcome Index was 84.
Conclusions: This study confirms that an excellent local control rate is achieved with PDR brachytherapy as treatment of lip carcinoma, with very limited late side effects and satisfactory functional outcomes. A multimodal approach should help to improve regional control.
Keywords: brachytherapy; lip cancer; pulsed dose rate; quality of life; radiation therapy; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- van Leeuwen M.T., Grulich A.E., McDonald S.P., McCredie M.R.E., Amin J., Stewart J.H., Webster A.C., Chapman J.R., Vajdic C.M. Immunosuppression and other risk factors for lip cancer after kidney transplantation. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. 2009;18:561–569. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0919. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gerbaulet A., Pötter R., Mazeron J.-J., Meertens H., Limbergen E., Mazeron J.-J. The GEC ESTRO Handbook of Brachytherapy. ACCO; Leuven, Belgium: 2002.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

