Variability of Urinary Creatinine in Healthy Individuals
- PMID: 33808539
- PMCID: PMC8003281
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18063166
Variability of Urinary Creatinine in Healthy Individuals
Abstract
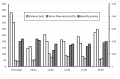
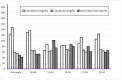
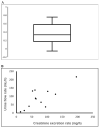
Many urinary biomarkers are adjusted for dilution using creatinine or specific gravity. The aim was to evaluate the variability of creatinine excretion, in 24 h and spot samples, and to describe an openly available variability biobank. Urine and blood samples were collected from 60 healthy non-smoking adults, 29 men and 31 women. All urine was collected at six time points during two 24 h periods. Blood samples were also collected twice and stored frozen. Analyses of creatinine in urine was performed in fresh urine using an enzymatic method. For creatinine in urine, the intra-class correlation (ICC) was calculated for 24 h urine and spot samples. Diurnal variability was examined, as well as association with urinary flow rate. The creatinine excretion rate was lowest in overnight samples and relatively constant in the other five samples. The creatinine excretion rate in each individual was positively correlated with urinary flow rate. The creatinine concentration was highest in the overnight sample and at 09:30. For 24 h samples the ICC was 0.64, for overnight samples it was 0.5, and for all spot samples, it was much lower. The ICC for urinary creatinine depends on the time of day of sampling. Frozen samples from this variability biobank are open for researchers examining normal variability of their favorite biomarker(s).
Keywords: 24 h urine; biobank; biomonitoring; creatinine; specific gravity; spot urine; variability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

