Neurocognitive Impairment in Severe Mental Illness. Comparative study with Spanish Speaking Patients
- PMID: 33808661
- PMCID: PMC8003381
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11030389
Neurocognitive Impairment in Severe Mental Illness. Comparative study with Spanish Speaking Patients
Abstract
Background: Serious mental illness (SMI) represents a category of psychiatric disorders characterized by specific difficulties of personal and social functioning, derived from suffering severe and persistent mental health problems.
Aims: We wanted to look into differences in cognitive performance among different SMI patients.
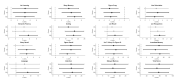
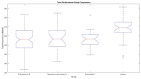
Methods: Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) screening was applied in one sample of SMI patients (n = 149) and another of healthy comparison participants (n = 35). Within the SMI sample, three different subsamples were formed: one with 97 patients with schizophrenia, a second with 29 patients with mood disorders, and a third with 23 patients with personality disorder. We performed a comparative study within and between groups.
Results: Analysis of covariance was performed. Significant differences were found for cognitive functioning including attention and memory.
Conclusions: RBANS can be recommended for the detection of neurocognitive deficits in psychiatric disorders, especially in Schizophrenia.
Keywords: Spanish; memory; mental health; neurocognitive; neuropsychology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- López M., Laviana M. Rehabilitación, apoyo social y atención comunitaria a personas con trastorno mental grave: Propuestas desde Andalucía. Rev. Asoc. Esp. Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;27:187–223. doi: 10.4321/S0211-57352007000100016. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization World Report on Disability: Summary 2011, WHO/NMH/VIP/11.01. [(accessed on 23 October 2020)];2011 Available online: www.refworld.org/docid/50854a322.html.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Arlington, VA, USA: 2013.
-
- De la Torre G.G., Suarez-Llorens A., Caballero F.J., Ramallo M.A., Randolph C., Lleó A., Sala I., Sanchez B. Norms and reliability for the Spanish version of the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) Form A. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2014;36:1023–1030. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2014.965664. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bazanis E., Rogers R.D., Dowson J.H., Taylor P., Meux C., Staley C., Nevinson-Andrews D., Taylor C., Robbins T.W., Sahakian B.J. Neurocognitive deficits in decision-making and planning of patients with DSM-III-R borderline personality disorder. Psychol. Med. 2002;32:1395–1405. doi: 10.1017/S0033291702006657. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

