Multi-Analytical Framework to Assess the In Vitro Swallowability of Solid Oral Dosage Forms Targeting Patient Acceptability and Adherence
- PMID: 33808875
- PMCID: PMC8003620
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030411
Multi-Analytical Framework to Assess the In Vitro Swallowability of Solid Oral Dosage Forms Targeting Patient Acceptability and Adherence
Abstract
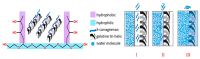
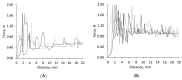
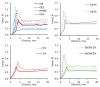
A lack of effective intervention in addressing patient non-adherence and the acceptability of solid oral dosage forms combined with the clinical consequences of swallowing problems in an ageing world population highlight the need for developing methods to study the swallowability of tablets. Due to the absence of suitable techniques, this study developed various in vitro analytical tools to assess physical properties governing the swallowing process of tablets by mimicking static and dynamic stages of time-independent oral transitioning events. Non-anatomical models with oral mucosa-mimicking surfaces were developed to assess the swallowability of tablets; an SLA 3D printed in vitro oral apparatus derived the coefficient of sliding friction and a friction sledge for a modified tensometer measured the shear adhesion profile. Film coat hydration and in vitro wettability was evaluated using a high-speed recording camera that provided quantitative measurements of micro-thickness changes, simulating static in vivo tablet-mucosa oral processing stages with artificial saliva. In order to ascertain the discriminatory power and validate the multianalytical framework, a range of commonly available tablet coating solutions and new compositions developed in our lab were comparatively evaluated according to a quantitative swallowability index that describes the mathematical relationship between the critical physical forces governing swallowability. This study showed that the absence of a film coat significantly impeded the ease of tablet gliding properties and formed chalky residues caused by immediate tablet surface erosion. Novel gelatin- and λ-carrageenan-based film coats exhibited an enhanced lubricity, lesser resistance to tangential motion, and reduced stickiness than polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-PEG graft copolymer, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), and PVA-coated tablets; however, Opadry® EZ possessed the lowest friction-adhesion profile at 1.53 a.u., with the lowest work of adhesion profile at 1.28 J/mm2. For the first time, the in vitro analytical framework in this study provides a fast, cost-effective, and repeatable swallowability ranking method to screen the in vitro swallowability of solid oral medicines in an effort to aid formulators and the pharmaceutical industry to develop easy-to-swallow formulations.
Keywords: acceptability; adherence; dysphagia; film coating; in vitro swallowability; solid oral dosage forms; swallowability index.
Conflict of interest statement
A.R.-S is the Chief Scientific Officer at Colorcon and S.M. is the Senior Manager in Product Development at Colorcon. The Colorcon had no role; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; but had input in the design of the study, writing of the manuscript and the decision to publish the results. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Esophageal transit of solid oral dosage forms - impact of different surface materials characterized in vitro and in vivo by MRI in healthy volunteers.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec 1;203:106926. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106926. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39383972
-
Influence of the geometry of 3D printed solid oral dosage forms on their swallowability.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Oct;167:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.07.009. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 34298113 Clinical Trial.
-
Creating Acceptable Tablets 3D (CAT 3D): A Feasibility Study to Evaluate the Acceptability of 3D Printed Tablets in Children and Young People.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 25;14(3):516. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030516. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35335892 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Acceptability and Preferences for Solid Oral Dosage Form Drug Product Attributes: A Scoping Review.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024 Jun 21;18:1281-1297. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S443213. eCollection 2024. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024. PMID: 38919378 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptability of Mini-Tablets in Young Children: Results from Three Prospective Cross-over Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Feb;18(2):263-266. doi: 10.1208/s12249-016-0639-3. Epub 2016 Oct 6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 27714698 Review.
Cited by
-
Physicochemical and Bioactivity Characteristics of Doxycycline Hyclate-Loaded Solvent Removal-Induced Ibuprofen-Based In Situ Forming Gel.Gels. 2023 Feb 3;9(2):128. doi: 10.3390/gels9020128. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36826298 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Inversion-Based Doxycycline Hyclate-Incorporated Borneol In Situ Gel for Periodontitis Treatment.Gels. 2023 Jul 7;9(7):557. doi: 10.3390/gels9070557. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504434 Free PMC article.
-
Clotrimazole-Loaded Borneol-Based In Situ Forming Gel as Oral Sprays for Oropharyngeal Candidiasis Therapy.Gels. 2023 May 15;9(5):412. doi: 10.3390/gels9050412. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37233003 Free PMC article.
-
Levofloxacin HCl-Loaded Eudragit L-Based Solvent Exchange-Induced In Situ Forming Gel Using Monopropylene Glycol as a Solvent for Periodontitis Treatment.Gels. 2023 Jul 18;9(7):583. doi: 10.3390/gels9070583. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris Interactive Inc . Pill-Swallowing Problems in America: A National Survey of Adults. Harris Interactive Inc. for Schwarz Pharma; New York, NY, USA: 2003. [(accessed on 17 March 2021)]. Available online: http://healthymoments.com/downloads/40percent.doc.
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Guidance Document: Size, Shape, and Other Physical Attributes of Generic Tablets and Capsules, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. [(accessed on 18 January 2020)];2015 Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

