Wound Healing Composite Materials of Bacterial Cellulose and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Immobilized Betulin Diphosphate
- PMID: 33809076
- PMCID: PMC8000300
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11030713
Wound Healing Composite Materials of Bacterial Cellulose and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Immobilized Betulin Diphosphate
Abstract
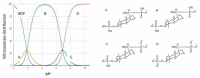
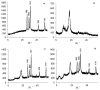
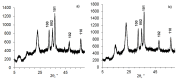
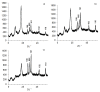
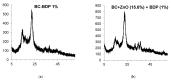
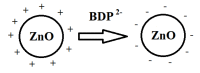
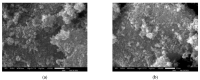
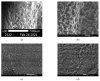
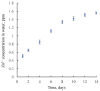
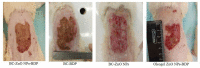
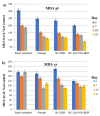
A design of new nanocomposites of bacterial cellulose (BC) and betulin diphosphate (BDP) pre-impregnated into the surface of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for the production of wound dressings is proposed. The sizes of crystalline BC and ZnO NPs (5-25%) corresponded to 5-6 nm and 10-18 nm, respectively (powder X-ray diffractometry (PXRD), Fourier-infrared (FTIR), ultraviolet (UV), atomic absorption (AAS) and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopies). The biological activity of the wound dressings "BC-ZnO NPs-BDP" was investigated in rats using a burn wound model. Morpho-histological studies have shown that more intensive healing was observed during treatment with hydrophilic nanocomposites than the oleophilic standard (ZnO NPs-BDP oleogel; p < 0.001). Treatment by both hydrophilic and lipophilic agents led to increases in antioxidant enzyme activity (superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase) in erythrocytes and decreases in the malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration by 7, 10 and 21 days (p < 0.001). The microcirculation index was restored on the 3rd day after burn under treatment with BC-ZnO NPs-BDP wound dressings. The results of effective wound healing with BC-ZnO NPs-BDP nanocomposites can be explained by the synergistic effect of all nanocomposite components, which regulate oxygenation and microcirculation, reducing hypoxia and oxidative stress in a burn wound.
Keywords: antioxidant properties; bacterial cellulose; betulin diphosphate; burns; wound dressings; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
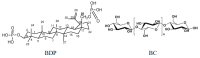

References
-
- Vorobyova O., Deryabina O., Malygina D., Plotnikova N., Solovyeva A., Belyaeva K., Melnikova N. Betulin-3,28-diphosphate as a Component of Combination Cytostatic Drugs for the Treatment of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments. Sci. Pharm. 2018;86:17. doi: 10.3390/scipharm86020017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

