Preclinical Evaluation of the Association of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor, Ribociclib, and Cetuximab in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 33809148
- PMCID: PMC7998503
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061251
Preclinical Evaluation of the Association of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor, Ribociclib, and Cetuximab in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpression is observed in 90% of human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck (SCCHN). Cell cycle pathway impairments resulting in cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and 6 activation, are frequently observed in SCCHN. We investigated the efficacy of ribociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, in combination with cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the EGFR, in HPV-negative SCCHN patient-derived tumor xenograft (PDTX) models. The combination of cetuximab and ribociclib was not significantly more active than cetuximab monotherapy in all models investigated. In addition, the combination of cetuximab and ribociclib was less active than ribociclib monotherapy in the cetuximab-resistant PDTX models. In these models, a significant downregulation of the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein was observed in cetuximab-treated mice. We also observed Rb downregulation in the SCCHN cell lines chronically exposed and resistant to cetuximab. In addition, Rb downregulation induced interleukin 6 (Il-6) secretion and the Janus kinase family member/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway activation that might be implicated in the cetuximab resistance of these cell lines. To conclude, cetuximab is not an appropriate partner for ribociclib in cetuximab-resistant SCCHN models. Our work has significant clinical implications since the combination of anti-EGFR therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors is currently being investigated in clinical trials.
Keywords: CDK4/6; cetuximab; resistance; retinoblastoma; ribociclib; squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
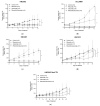
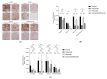



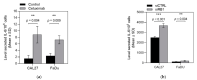
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

